- Gestational diabetes - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9012-gestational-diabetes)
- Definition & Facts of Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/gestational/definition-facts)
- Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gestational-diabetes)
- Gestational diabetes mellitus - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4404472/)
- Gestational diabetes symptoms - (https://www.diabetes.org.uk/about-diabetes/gestational-diabetes/symptoms)
- Gestational diabetes diet - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007430.htm)
- Risk factors for progression from gestational diabetes to postpartum type 2 diabetes: a review - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7855576/)
- Disparities in the risk of gestational diabetes by race-ethnicity and country of birth - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4180530/)
- Symptoms of gestational diabetes - (https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-complications/gestational-diabetes/symptoms-gestational-diabetes)
- Blood Glucose and Exercise - (https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/blood-glucose-and-exercise )
- Dietary Recommendations for Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/dietary-recommendations-for-gestational-diabete)
- Breastfeeding and Diabetes - (https://diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/pregnancy/diabetes-breastfeeding)
Blood Sugar Converter |
This Calculator is based on the guidelines provided by World Health Organization.
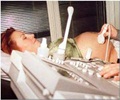
How to Test for Diabetes in Pregnancy
You'll need to take a special blood test called the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Here's how it works:- You fast (don't eat) overnight.
- Go to the diagnostic lab, and they will check your fasting blood sugar level.
- You drink a sweet liquid containing 75 grams of glucose.
- Two hours later, they check your blood sugar again.
Facts about Pregnancy Diabetes:
| ❖ | The child born to a mother with GDM is at a high risk for glucose intolerance, diabetes and becoming obese in future. |
| ❖ | The baby may be born with breathing disorders and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). |
| ❖ | The most common problem associated with gestational diabetes is macrosomia, in which, baby is born weighing more than 4 kg. |
| ❖ | Giving birth to a heavier baby may be a problem at the time of delivery, and hence, cesarean delivery maybe required. |
| ❖ | Congenital malformation is one of the reasons why babies die when born to women with gestational diabetes. |
Diet Tips for Gestational (Pregnancy) Diabetes:
It is important for a woman with Gestational (Pregnancy) Diabetes to follow a healthy diet plan and keep her blood sugar (glucose) level under control.- Include fat and protein in moderate amounts. Some of the protein rich foods include meat, fish, dry beans, eggs, and nuts.
- Taking whole fruits is a healthier choice than drinking juice.
- Your carbohydrate intake must account for less than half of the calories you take. Eat sugar-free sweets.
- Cut down on hamburgers and cheese that are rich in saturated fats.
- Spaced-out, balanced meals help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Pay attention to carbohydrate content in your daily diet and choose whole grains over refined options.
- Drinking plenty of water helps your body function optimally and can also help reduce cravings for sugary drinks.
References:
- clinical.diabetesjournals.org/content/23/1/17.full.pdf
- ww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc2582643/
- care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/suppl_1/s88.full#sec-8
- www.hawaii.edu/hivandaids/Gestational%20Diabetes.pdf
- http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/007430.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/gestational.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/prevent-complications.html
FAQs
1. Which doctor should I visit for for gestational diabetes?
You should initially consult with your obstetrician (OB-GYN) for gestational diabetes management. Depending on your specific needs, they may also refer you to other specialists such as an endocrinologist for further guidance and treatment.
2. Why is testing blood sugar important in pregnancy?
Without specific testing, gestational diabetes can often go undetected until complications arise. The symptoms and signs of diabetes maybe subtle such as excessive thirst, increased urination, and unusual tiredness.
3. What is the incidence of Gestational Diabetes?
The incidence of diabetes that first manifests during pregnancy, known as gestational diabetes, varies from 2% to 4% in the general population. However, this rate may be significantly higher among south Asian women.
4. What complications can occur if diabetes is not controlled?
The major complications of diabetes are heart disease, stroke, blindness, eye problems, kidney diseases, nerve damage, amputations, preeclampsia, and birth defects.
5. Will I require insulin jabs to control my sugar?
Yes, sometimes it maybe required to control the blood sugar level. If diet does not help, the insulin maybe required to help overcome fetal and maternal complications.
6. Will I need Insulin all life?
No, not at all. Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition, as mentioned previously
7. What percentage of women with gestational diabetes will have diabetes after the pregnancy?
The blood sugar level will usually return to normal after delivery. However, around 50% of women with gestational diabetes go on to develop type 2 diabetes.
8. Does ethnicity play a role?
Yes, Ethnicity plays a major role in gestational diabetes. Women of the following ethnic groups have higher chances of having gestational diabetes:
- African Americans
- Hispanic or Latino Americans
- American Indians
- South Asian
9. What complications can occur due to gestational diabetes to the mother?
Uncontrolled gestational diabetes can increase risks of birth defects, and preeclampsia for the mother. Larger babies (macrosomia) can lead to delivery complications..
10. What problems can babies have when they are borne of mothers with gestational diabetes ?
Most babies born to mothers with controlled gestational diabetes are healthy. However there are potential risks to the baby including breathing difficulties, low blood sugar, and increased birth weight.
11. What are the symptoms of gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes often manifests without noticeable symptoms, highlighting the importance of testing for early detection and management. However, when symptoms do appear, they can include increased thirst, frequent urination, dry mouth, fatigue, blurred vision, or genital itching or thrush.
12. Can exercise help control gestational diabetes?
Yes, regular exercise helps your body use insulin more effectively, keeping blood sugar levels in check.
13. What happens during a gestational diabetes test?
During a gestational diabetes test, you'll need to fast overnight, avoiding any food intake. Then, you'll head to the diagnostic lab, where they'll measure your fasting blood sugar level. Following this, you'll consume a sweet liquid containing 75 grams of glucose. After waiting for two hours, your blood sugar will be checked again to assess your body's response to the glucose intake. This process helps healthcare providers determine whether you have gestational diabetes.
14. How often will I need to monitor my blood sugar?
The frequency depends on your individual needs and how well your blood sugar is controlled. Your doctor will advise you on a monitoring schedule.
15. Can I still eat sweets if I have gestational diabetes?
It's best to limit sugary treats. However, occasional indulgence is okay with proper portion control and planning within your dietary recommendations.
16. Is breastfeeding safe with gestational diabetes?
Breastfeeding is safe and encouraged for women with gestational diabetes. It can actually help lower blood sugar levels.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email

























I had my Glucose test done today 100 grams Fasting : 81 1 hour: 172 2 hour: 127 3 hour : waiting on my last result Is this is high ?