- Gestational diabetes - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9012-gestational-diabetes)
- Definition & Facts of Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/gestational/definition-facts)
- Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gestational-diabetes)
- Gestational diabetes mellitus - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4404472/)
- Gestational diabetes symptoms - (https://www.diabetes.org.uk/about-diabetes/gestational-diabetes/symptoms)
- Gestational diabetes diet - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007430.htm)
- Risk factors for progression from gestational diabetes to postpartum type 2 diabetes: a review - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7855576/)
- Disparities in the risk of gestational diabetes by race-ethnicity and country of birth - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4180530/)
- Symptoms of gestational diabetes - (https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-complications/gestational-diabetes/symptoms-gestational-diabetes)
- Blood Glucose and Exercise - (https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/blood-glucose-and-exercise )
- Dietary Recommendations for Gestational Diabetes - (https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/dietary-recommendations-for-gestational-diabete)
- Breastfeeding and Diabetes - (https://diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/pregnancy/diabetes-breastfeeding)
Medically, Gestational (jes-TAY-shun-ul) Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is defined as glucose intolerance, which is diagnosed during pregnancy. It is reported to affect approximately 7% of all pregnancies. GDM can adversely affect both the mother and the baby; hence a diagnosis, if made, should be taken seriously.
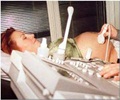
The risk factors for GDM include – A family history of diabetes, obesity or testing positive for glucose in the urine. Most pregnant women will undergo screening to check the blood glucose level. If the readings are high, they will be advised to undergo an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Blood samples are taken while fasting and also during one, 2 and 3 hours after having 100 gms of glucose. These samples are tested in the laboratory and the readings are interpreted.
| Sample drawn after 100-gram glucose drink (glucose load) | |
| Time of Sample Collection | Target LEVEL |
| Fasting* (prior to glucose load) | 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L) |
| 1 hour after glucose load | 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) |
| 2 hours after glucose load | 155 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L) |
| 3 hours after glucose load* | 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) |
| INDICATION: If two or more values meet or exceed the target level, gestational diabetes is diagnosed. | |
The National Institutes of Health Diabetes Data Group (NDDG) from the USA (Diabetes 1979;28:1039) and the values established by Carpenter and Coustan (Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982;144:768-73) uses a 100 gram glucose load. Their diagnosis is based on four measurements (fasting, 1, 2 and 3 hr. glucose levels).
Over the years different investigators have come up with different values with small variations as shown in the chart below.
| NDDG(1979) | Carpenter & Coustan (1982) | Sacks et al (1989) | |
| Fasting | 105 | 95 | 96 |
| 1 hour | 190 | 180 | 172 |
| 2 hour | 165 | 155 | 152 |
| 3 hour | 145 | 140 | 131 |
References:
- clinical.diabetesjournals.org/content/23/1/17.full.pdf
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc2582643/
- care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/suppl_1/s88.full#sec-8
- www.hawaii.edu/hivandaids/Gestational%20Diabetes.pdf
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email


















I had my Glucose test done today 100 grams Fasting : 81 1 hour: 172 2 hour: 127 3 hour : waiting on my last result Is this is high ?