- Jales, R., Hirata, S., Attalah, Á., Sá-Caputo, D., Arnóbio, A., Frederico, É.H., Bernardo-Filho, M. and Saconato, H. (2015) Scalp Psoriasis: Systematic Review Comparing Topical Treatments and Placebo. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 5, 142-150. - - (http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2015.52017)
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 19th edition. - (http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2015.52017)
- Hermanns-Lê T, Berardesca E, Piérard GE, Lesuisse M, Piérard-Franchimont C. Challenging Regional Psoriasis and Ustekinumab Biotherapy: Impact of the Patterns of Disease. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 2012 (2012), Article ID 413767 - (http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/413767)
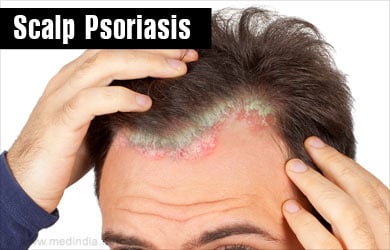
What is Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is a type of skin disorder that causes lesions on the scalp. Though several treatments are available, it cannot be completely cured and can recur after treatment.
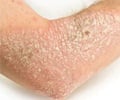
Psoriasis is a common skin condition that causes well-demarcated lesions with sharp margins covered with scales. The lesions are circular, oval or have geographic shapes. The scalp is the most common part of the body that is affected by psoriasis. Psoriasis also affects several other parts of the body like elbows, knees, gluteal cleft, nails and joints.
What are the Causes of Scalp Psoriasis?
Our skin constantly produces new cells, and sheds off the top layer consisting of old cells. In psoriasis, more number of cells are produced than what are shed. This results in areas of thickened skin with a superficial scaly appearance.
Like other types of psoriasis, scalp psoriasis appears to be an autoimmune reaction that has a genetic basis. It often manifests in the presence of certain factors like emotional factors, pregnancy, stress and intake of certain drugs which include antimalarial drugs, lithium, NSAIDs and the blood pressure medications, beta blockers and ACE inhibitors.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis can vary from mild to severe. It is characterized by the following:
- Presence of well-demarcated single or multiple lesions on the scalp
- The lesion is covered with dry scales, which may get caught in the hair
- It may extend behind the ears, back of the neck or on the forehead
- Some lesions may be crusted
- Itchiness is present. However, scratching worsens the condition
- There may be bleeding or loss of hair due to the itching
- Similar lesions may be noted in other parts of the body that are commonly affected by psoriasis
- The patient may feel depressed due to the cosmetic problem caused by the condition

How is Scalp Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Scalp psoriasis is diagnosed based on history and physical examination of the patient.
Sometimes, a skin biopsy may be done if there is doubt in the diagnosis.
A common condition that can cause confusion in the diagnosis due to a similar appearance is seborrheic dermatitis or dandruff affecting the scalp. On careful examination, it will be noticed that scales are greasy in seborrheic dermatitis while they are silvery and dry in psoriasis.
How do you Treat Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis is treated with local or systemic medications. Combinations of various treatment are often used depending on the extent of the condition. Several of these drugs cannot be used in pregnant patients.
Local formulations like oils, lotion, solution, creams and shampoos are available to apply to the lesions. These should be used only as instructed by the prescribing doctor. These may contain:
- Corticosteroids like clobetasone, betamethasone, halcinonide, and fluocinolone acetonide help reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis. In case of a single lesion, the corticosteroid can be directly injected into the lesion. The patient must also be alerted that the lesions can recur if the medication is suddenly stopped without consulting the physician
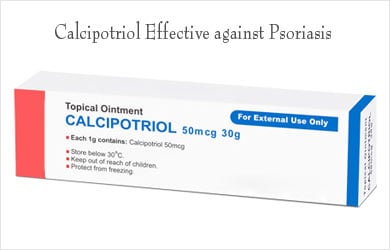
- Calcipotriol, which is a form of vitamin D and is found to be effective in psoriasis
- Coal tar and salicylic acid, which break down the thickened lesions of psoriasis. Shampoos containing salicylic acid and coal tar are available. The shampoo should be rubbed into the scalp and is not meant for the hair. The scales should be taken off gently and not scratched out
- Tazarotene, which is a form of vitamin A
- Anthralin, which slows formation of new cells
Oral treatments include:
- Acitretin, which is a form of vitamin A
- Methotrexate and cyclosporine
Biological agents, which act on the inflammatory process of psoriasis. They are given in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Their cost-effectiveness and side effects should be considered. These include:
- Alefacept, which is given by injection into the vein or the muscle
- Etanercept, adalimumab and ustekinumab, which are injected under the skin
- Infliximab, which is injected into the vein
Ultraviolet light is sometimes used with some of the medications to treat psoriasis. However, it should be remembered that ultraviolet light can increase the chances of skin cancer.
Health Tips
- Stress can worsen psoriasis. Therefore, reducing stress can help keep psoriasis under control.
- Do not scratch your scalp if you suffer from psoriasis. New lesions will appear at sites that you have scratched. This is referred to as Koebner’s phenomenon.
- Use medications strictly as per the advice of your prescribing physician.
- A healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables could help in keeping the disease under control.

- Excessive exposure to sunlight can worsen the condition, and should, therefore, be avoided.