Glossary
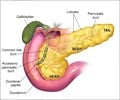
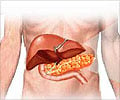
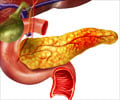
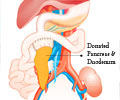
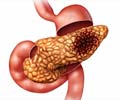
Pancreas: A glandular organ located in the abdomen. It makes pancreatic juices, which contain enzymes that aid in digestion. It produces several hormones, including insulin. The pancreas is surrounded by the stomach, intestines, and other organs.Insulin: A hormone made by the islet cells of the pancreas. Insulin controls the amount of sugar in the blood by moving it into the cells, where it can be used by the body for energy.
Glucagon: A hormone produced by the pancreas that releases the body's stored sugar (glycogen) into the blood. An injectable form of glucagon, which can be bought in a drug store, is sometimes used to treat insulin shock. The glucagon is injected and quickly raises blood glucose levels.
Duodenum – the first part of the small intestine. It is intimately associated with the pancreas.
Exocrine – the part of the pancreas that forms and secretes digestive juices into the intestine through its ducts.
Endocrine – a gland that does not have ducts to carry its secretion to the target. They are called ductless glands. The secretions are directly released into the bloodstream to be carried.
Radiotherapy: The use of electromagnetic or particulate radiation in the treatment of disease.
Chemotherapy: Treatment with anticancer drugs.
Hepatitis: An infection or inflammation of the liver.
Pancreatectomy: Surgical removal of the pancreas.
Mutation: An alteration in the person’s DNA which may or may not cause cancer
Hereditary cancers: Cancers that run in families due to the presence of mutations in their DNA
Adenocarcinoma: A cancer where the cells form glands and are arranged in glandular structures.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email













my father 72yrs age 10yrs before he had one mass in left throat after we make operation and after biopsy there was a cancer infection after that we give him 1 month radiation and six chemo.now on right side there is another small grow in throatt and abdomen usg report shows CBD dilated 12mm and head of pancreas one mass exist.now his bilirumin is 10.2mg and not able to eat and itching full body.some fever(101 F)is there with out any surgery how i can keep him quite normal he also diabetic(avg pp220)please give some medicine name that can help him to reduce jundis his eyes is yellow and urin also very yelloish.please help me i am a poor family not afford any surgery and i wish only how much day he lives he should live without pain with any medicine.thanks