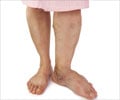
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
In deep vein thrombosis, there occurs an obstruction of blood returning to the heart and it leads to a backup of blood in the leg. Redness, warmth, tenderness, swelling occurs.
Any trauma to a superficial vein causes a small blood clot to form. Affected vein is often palpable as a thick vessel. Inflammation of the vein and surrounding skin causes:
- Redness
- Warmth
- Tenderness
- Swelling
In deep vein thrombosis, there occurs an obstruction of blood returning to the heart and thus leads to a backup of blood in the leg. This can cause:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Warmth
- Redness
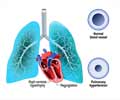
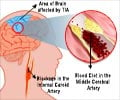
DVT may also be silent without any of these symptoms and this can be more dangerous as it may throw up a clot that may get lodged in the vessel of lungs causing acute breathing problems (called pulmonary embolism). The consequences of such a clot can sometimes be very grave for the person.
Cellulitis and certain infections of leg may mimic a DVT. Sometimes there occurs a massively swollen leg with pitting edema, pain, and blanching, a condition known as phlegmasia alba dolens. In advanced cases a painful blue leg develops, the condition is called phlegmasia cerulea dolens. If uncorrected, gangrene ensues and the leg may require amputation