- Contact Dermatitis - (https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/contact-dermatitis/)
- Contact dermatitis: Overview - (https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/eczema/contact-dermatitis)
- Diagnosis and Management of Contact Dermatitis - (http://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/0801/p249.html)
- Allergic contact dermatitis - (https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/allergic-contact-dermatitis/)
- Know About Contact Dermatitis - (http://acaai.org/allergies/types/skin-allergies/contact-dermatitis)
- What is contact dermatitis? - (http://www.britishskinfoundation.org.uk/skininformation/atozofskindisease/contactdermatitis.aspx)
What is Contact Dermatitis?
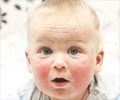
Contact Dermatitis is a reaction of the skin in the form of skin rashes on coming into contact with certain allergens or irritants. It causes the skin to itch, inflame, become red and may lead to blisters.
It can be caused due to following factors:
- Physical contact with a substance which acts as an irritant or
- Exposure to an allergen; the allergen produces an allergenic reaction which causes the immune system to respond as a skin reaction.
Dermatitis is also known as eczema. Thus, contact dermatitis is also known as contact eczema.
What are the Causes of Contact Dermatitis?
Some of common causes are listed below:
- Common allergens
- Acids
- Alkalis like soaps, detergents, household ammonia and cleaners
- Bromise
- Chlorine
- Cosmetics that include perfumes, dyes and some oils
- Dusts of lime, arsenic and wood.
- Hydrocarbons such as crude petroleum, lubricating oil, mineral oil, paraffin, asphalt and tar.
- Iodine
- Insecticides
- Fabrics like wool, polyester and dyes
- Metal salts like calcium chloride, zinc chloride, copper, mercury, nickel and silver
- Plants such as ragweed, poison oak, poison ivy and pine
- Coloring agents
- Rubber agents and rubber products
- Soot
Being in certain professions and hobbies can also cause contact dermatitis. For example, hair dressers, gardeners, cleaners, machine operators and construction workers are possible ways.
What are the Types of Contact Dermatitis?
There are four main types of contact dermatitis:
1. Allergic contact dermatitis:
This occurs when the substance or the allergen triggers an immune reaction in the skin. These reactions could be triggered by substances, which enter a body, either through medicine, foods, flavorings or dental procedures. Compared to irritant contact dermatitis, the skin may take 48 to 96 hours to develop a reaction in allergic contact dermatitis.
The common allergenic substances or allergens include:
- Personal care products – deodorants, cosmetics, sunscreen agents
- Nickel – a constituent in jewellery, buckles, buttons
- Rubber – including latex gloves
- Medications – some categories of antibiotic creams and oral antihistamines
- Poison ivy – This plant contains a substance, urushiol, which causes erythema or reddening of the skin in patches
- In children, the allergens could be diapers, baby wipes, and clothes with dyes

2. Irritant contact dermatitis:
This is the most common type. It is a non-allergenic reaction that occurs when a substance causes irritation and damages the outer protective layer of skin. This reaction develops immediately and if the skin has an open wound, the irritant substance enters the skin layer and causes irritant contact dermatitis.
A person suffering from atopic eczema is at an increased risk of irritant contact dermatitis.
The most common irritants include:
- Fertilizers
- Soaps and shampoos
- Plants
- Cement
- Powder and dust
- Perfumes and preservatives in cosmetics
3. Photoallergic contact dermatitis:
This type occurs when an irritant or allergen causes a reaction, only on exposure to sun. Examples of substances that cause this type of reaction are sunscreens, perfumes or deodorants and shaving lotions.
4. Contact Urticaria:
This is the least common form of contact dermatitis. It is also known as hives. In this type, swelling and redness occur immediately on contact with the irritant and it does not last long.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Contact Dermatitis?
The symptoms of contact dermatitis can range from mild redness to severe pain and scaling of skin, which can restrict daily activities and cause social awkwardness.
Contact dermatitis is usually seen in areas of the body that have been in contact with the substance causing irritation or allergy.
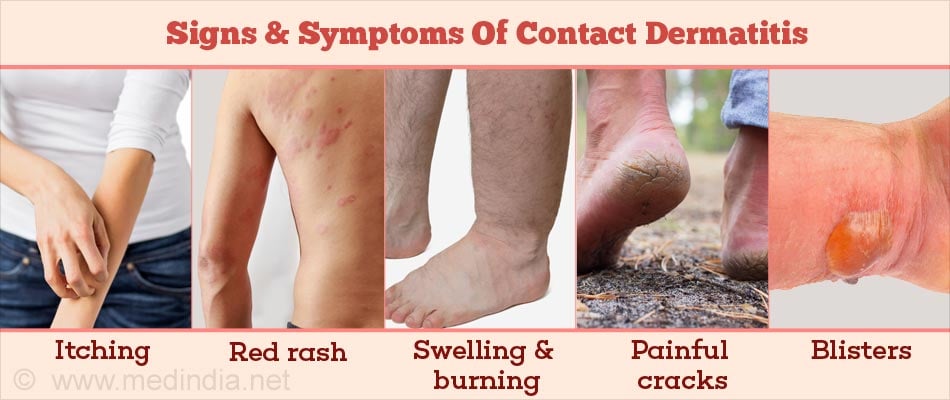
The typical signs and symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
- Itching
- Red rash
- Swelling and burning
- Dry, scaly skin
- Painful cracks
- Blisters
How do you Diagnose Contact Dermatitis?
The health care provider or dermatologist would closely examine the skin or rash and then ask for information about your profession or contact with any known allergens.
Depending upon the skin reaction, its appearance and other symptoms, the healthcare provider may diagnose the reaction as contact dermatitis.
Once diagnosed as contact dermatitis, the doctor would try to identify the irritant(s) or allergen(s) which trigger the reaction.
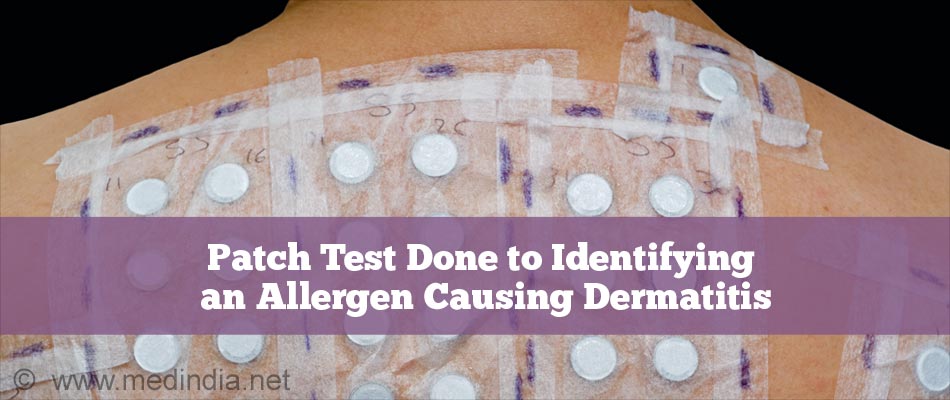
Testing for Allergens
Allergy testing is usually performed by an allergist. The most common allergy test for identifying an allergen causing dermatitis is patch testing.
This patch test is conducted to check for sensitivity of a person to potential allergens. In this test, selected chemicals are applied on a patch and the patch is then applied to the back area, where there are no symptoms. The patches are left as is for 48 hours, after which the patches are removed and the doctor checks if the patches show any reaction. If there is any inflammation, allergy to that particular chemical is confirmed.
Testing for Irritants
Identifying an irritant could be very challenging and not very reliable.
One of the tests to assess the effect of cosmetics is a repeated open application test (ROAT). In this test, the substance is applied on the same skin area, twice a day, for 5-10 days and the skin reaction, if any, is observed.
What are the Complications of Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis can lead to multiple complications, as listed below:
Bacterial infection - This occurs if the affected area is repeatedly scratched or the skin is cracked. The area becomes wet because of oozing liquid, encouraging the growth of bacteria and fungi.
Impacting Social life - Suffering from contact dermatitis may cause a person to feel depressed and socially withdrawn because of the symptoms and fear of social stigma.
How do you Treat Contact Dermatitis?
The various methods to treat contact dermatitis or to reduce the symptoms include:
- Reduce exposure to the irritant for example, by wearing gloves and avoiding contact with irritant chemicals
- Use of emollients or moisturizers for symptomatic relief
- Avoid allergens
- Medication treatment:
- Steroid creams or ointments: These soothe the rash caused due to contact dermatitis and reduce the inflammation. The product may be applied one or two times a day, for two to four weeks. Always consult your doctor before using steroid creams or ointments.
- Oral medications: The health care provider may prescribe oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation or antihistamines to provide relief from itching or antibiotics to cure the bacterial infection.

- Other methods:
- Phototherapy or photochemotherapy – This is also known as PUVA. It is a type of ultraviolet radiation therapy, for treating skin diseases. PUVA is a treatment using combination of Psoralens (P) and exposure to UVA (long wave ultraviolet radiation). The affected area is exposed to ultraviolet light to help improve its appearance.
- Immunosuppressant therapy – Medications such as cyclosporin, methotrexate, and azathioprine are prescribed to reduce inflammation by suppressing the immune system
What Precautions Must be Observed When suffering From Contact Dermatitis?
- Try to identify the substance which causes the reaction and avoid contact with it
- Use moisturizing lotions several times a day
- Consult a skin specialist if symptoms worsen and begin to affect your activities