About
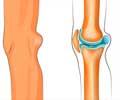
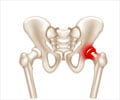
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that leads to an increased risk of fractures.
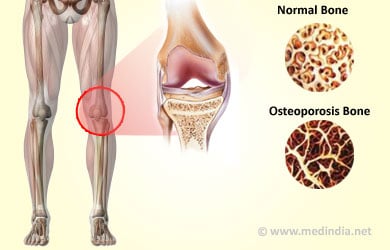
In osteoporosis, the bone mass is reduced and the bones are porous, thereby resulting in weakness of the skeletal system of the body.
Osteoporosis affects millions of people throughout the world. Women are four times more likely than men to develop the disease.
Bones are living, growing tissue in the body. They are made mostly of collagen, a protein that provides a soft framework, and calcium phosphate, a mineral that adds strength and hardens the framework.
Throughout youth, the body uses proteins and calcium to promote growth of bones. If the calcium intake is not sufficient or if the body does not absorb enough calcium from the diet, bone development may suffer. Calcium and phosphate may be reabsorbed back into the body from the bones, in which case the bone tissue becomes weaker. This results in brittle, fragile bones that can be easily broken.
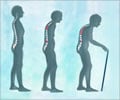
Usually, the loss occurs gradually over an extended period of time (years) and most of the time, a person will sustain a fracture before becoming aware that the disease is present. By the time this occurs, the disease is in its advanced stages and damage is profound. Therefore, osteoporosis is often known as ‘the silent thief’ because bone loss occurs without symptoms and the progressive loss and thinning of bone tissue happens over many years.
A bone mineral density test is the best way to check the bone health.
Eating a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, exercising and giving up smoking can help prevent osteoporosis. If needed, medicines can also be taken to treat osteoporosis.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email