- Ten top issues for women's health - (http://www.who.int/life-course/news/2015-intl-womens-day/en/)
- Women's Health - (https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/womenshealth.html)
- What health issues or conditions affect women differently than men? - (https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/womenshealth/conditioninfo/pages/howconditions.aspx)
- Heart disease in women: Understand symptoms and risk factors - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/in-depth/heart-disease/art-20046167)
- Cancer Facts for Women - (http://www.cancer.org/healthy/findcancerearly/womenshealth/cancer-facts-for-women)
- Women and Mental Health - (http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/women-and-mental-health/index.shtml)
- How Diabetes Differs for Men and Women - (http://www.diabetesforecast.org/2011/oct/how-diabetes-differs-for-men-and-women.html)
- About Your Thyroid - (http://www.empoweryourhealth.org/endocrine-conditions/thyroid/about_your_thyroid)
- Iron-deficiency anemia - (http://womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/anemia.html)
- Women's health: Prevent the top threats - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/womens-health/art-20045466?pg=2)
Women’s Top 10 Health Issues
Women experience health issues and conditions, from pregnancy and menopause to gynecological conditions. Several of these health issues are on account of different metabolic and endocrine systems. Many women tend to neglect their health as they are busy caring for others. However, it is important to stay on top and have a system of self-care to experience positive health and well-being. Certain health issues if detected early can be tackled better. It is important for all women to be tuned into their bodies and detect early warning signs of major health issues.
Women’s health issues suffer from systemic neglect within healthcare systems and public discourse, especially in developing nations. According to Dr. Flavia Bustreo, Assistant Director-General for Family, Women’s and Children’s Health through the Life-course, World Health Organization (WHO); even twenty years after countries signed pledges in the 1995 Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, women continue to suffer from major health issues, which often go unnoticed and unaddressed. Women’s right to health access and equity is a major issue in developing countries with lop-sided gender justice. Governments and public health systems must create awareness on the importance of women’s health issues and the need for timely addressal.

Here’s the list of top ten health issues faced by women in both developed and developing nations.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of women’s deaths across the world. Heart disease is often undetected and under-diagnosed in women. Women tend to manage and live with symptoms like breathlessness, tiredness and fatigue for years before they get an accurate diagnosis. Women often end up in the emergency long after the heart has already suffered significant damage. Some women experience heart attacks without pain and experience symptoms unrelated to heart disease such as:
- Discomfort in the jaw, shoulder, neck, back or abdomen
- Breathlessness
- Right arm pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Fatigue
Women experiencing any of these symptoms need to seek medical help to rule out the impending crisis.
Heart disease risk factors in women include:
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome that include high blood glucose levels, high blood pressure and elevated triglycerides
- Mental stress and depression
- Low estrogen levels after menopause or hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus)
- Complications during pregnancy

Cancer
Breast, ovarian, endometrial and cervical cancers are the leading killer of women globally. If cancers are detected early, there is a good chance of remission and cure. Women need to educate themselves with the help of doctors to understand their personal risks due to genetic and familial factors.
Breast cancer risks include increasing age, genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, family history of the disease, early onset of menstruation or menopause, not having conceived and use of hormones. Women above the age of 40 must opt for annual screening and mammograms along with regular self-examination of breasts.
Ovarian cancer risks include age, non-conception of children, unexplained infertility, bearing children after the age of 30 and hormone-replacement therapy. A pelvic exam should be on every woman’s health check-up routine. Women must immediately seek medical help if they experience symptoms like abdominal swelling, digestive issues, abdominal or pelvic pain and heaviness in the pelvis.
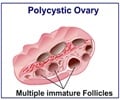
Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women over 55 years of age and older. Use of estrogens without progesterone, not having children, late conception, early menstruation and late menopause are significant risks. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOD) and obesity are other clear risks. Women must be aware of early symptoms of unusual spotting or bleeding.
Cervical cancer can affect any women who have had active sexual relations. The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is transmitted during sex and causes cervical cancer. Cervical cancer risks also include smoking and poor nutrition. Cervical cancer testing needs to begin as early as 21. The pap smear test is the best way to early detection and treatment. Even women who have received the HPV vaccination need regular screening.
Gynecological Health Issues
Women face disruptive health due to a number of gynecological issues like menstrual problems (heavy bleeding, pain, cramps, nausea, fatigue) and irregularities, urinary tract issues like frequent infections and inflammatory disorders, fertility related issues like uterine fibroids, PCOD, endometriosis (inflammation of the endometrial lining) and primary ovarian insufficiency. Being aware of one’s body type and symptoms and seeking immediate medical help is a must to avoid unnecessary risks and complications.

Women also face some issues related to pregnancy like miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm labor and premature birth. Women in developing countries often do not get medical access immediately, and this leads to a number of issues like infections, blood loss and even death. Pregnancies in rural areas are often handled by non-medical people who may not have sufficient knowledge or skills. There is a dire need to strengthen primary maternity care in developing nations.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is the leading cause of fractures among post-menopausal women worldwide. One in two women over the age of 50 suffers from an osteoporotic fracture. Hip fracture risk equals the combined risk of breast, uterine and ovarian cancer. Women are twice as likely to suffer from osteoporosis on account of the fact that women have thinner bones. During menopause, the hormone estrogen takes a dip causing bone loss, weakening, and consequent stress fractures.
Knowing the risk factors especially during menopause can go a long way in preventing disabling fractures. Women undergoing menopause must increase their daily dietary calcium and vitamin D intake. Getting sufficient sunlight during the day is a good way to get vitamin D. Exercise helps prevent osteoporosis. Annual bone-mineral density tests are recommended to stay warned and prepared. In some cases, the orthopedic doctor may recommend osteoporosis medications like risedronate sodium. Younger women with amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) may be put on hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to prevent early osteoporosis.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is most common among women above 45. It is believed that the process of menopause is a trigger for osteoarthritis. This disease occurs when the cartilage tissue cushioning the ends of bones in the joints, breaks down and wears out. The cartilage may totally wear out leaving the ends of bones rubbing against each other causing severe, debilitating pain. Osteoarthritis commonly affects the knees and hips though it also affects the hands, spine and wrists.
There is no known preventive measure for osteoarthritis except keeping fit and active. The best way to avoid pain is exercise especially joint strengthening exercises, motion exercises and low-impact activities like brisk walking. Most women seek non-drug relief like massages, hot and cold compresses, acupuncture etc. In cases where mobility is severely affected and restricts life activities, one may go for knee/hip replacement. Globally there are more women seeking joint replacement than men.
Psychiatric Disorders
Though mental disorders affect both men and women, medical researchers are now able to linkup hormone systems, endocrine systems and psychosocial factors to mental health. Women are more prone to certain types of psychiatric disorders especially during times of physical stress such as pregnancy and post-partum period. Depression is especially common during pregnancy and post-partum period.
Clinical and contextual depression are often experienced among women in developed and developing nations. Bipolar disorder and schizophrenia also affect women more than men. Seeking the help of counselors and psychiatrists is the best way to overcome mental health issues. Women are encouraged to be aware of their moods and seek help whenever necessary.
Diabetes
American Diabetes Association finds that women have unique health concerns because pregnancy can often bring about gestational diabetes. Diabetes during pregnancy can lead to complications like miscarriages or birth defects. Gestational diabetes raises women’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Women with diabetes are twice as likely to suffer from early heart attacks. Kidney disease also affects women worse than men. Researchers believe there is a correlation between lower estrogen levels and diabetic kidney disease that indicates higher levels of testosterone affects kidneys in diabetes.
According to Legato and a group of doctors who published a list of recommendations for women with diabetes in Gender Medicine, women with diabetes must get frequent checkups for heart, kidney and eye health. Given that gestational diabetes and PCOD increase a woman’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes, such women must frequently test their blood glucose levels along with quarterly HBA1C (glycosylated hemoglobin). Lifestyle choices like low-fat diet, sufficient exercise, staying off alcohol and cigarettes can also improve health outcomes for women with diabetes.
Endocrine Disorders
Endocrine disorders like thyroid and other hormonal imbalances frequently affect women. Being aware of one’s body and its changes is helpful for early detection and seeking medical help. Untreated endocrine disorders can adversely impact one’s overall health and well-being and often leads to other complications like type 2 diabetes and elevated cholesterol levels.

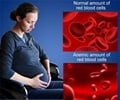
Anemia
Anemia or low hemoglobin levels are more common in developing countries where women lack sufficient nutrition and dietary requirements like iron and folic acid. Anemia can also be caused by heavy bleeding during menstrual periods or other underlying disorders. Many women go through phases of anemia during and after pregnancy. Most often women ignore symptoms of anemia like pallor, fatigue, shortness of breath, headache, chest pain, irregular heartbeat and listlessness.
Anemia can be avoided by taking sufficient iron in the diet and via supplements along with vitamin B12 or folate. A simple hemoglobin count can indicate anemia and one can take appropriate measures to correct it.
Stroke
According to the National Stroke Association, USA, each year 55,000 more women suffer from a stroke more than men. There are several reasons correlated to women’s risk of strokes which include obesity, family history, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking and drinking. Additionally women who are on birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and suffer from migraines are at a greater risk. It is also believed that pregnancy increases a woman’s risk as it elevates heart rate and blood pressure.
Some simple measures can help prevent strokes in women up to some extent. Women who suffer from a migraine must stay off smoking and alcohol. Pregnant women must be monitored for blood pressure and heart rate. Women taking birth control pills and those on HRT must regularly check their blood pressure (minimum once a week). Women who experience sudden discomfort, severe headache or sudden giddiness must immediately get medical attention.
While some of the above health issues are not totally preventable due to hereditary and genetic causes, one can still take precautions and make simple lifestyle changes to live a healthy life. Eating a balanced, nutritious diet along with sufficient exercise and cutting back on alcohol and smoking can ensure prevention to some extent. All women are encouraged to listen to their body signals and take proper care to seek medical help whenever required. Even minor bodily changes can signal the onset of a major disease and hence women should immediately seek medical attention. A disease caught in the early stage has a better chance of cure and recovery. Staying positive and connected to family and friends goes a long way in increasing immunity and disease fighting power.

Health tips for working woman!
- Stay active throughout the day
- Store your house with healthy snacks
- Create an effective exercise pattern
- Drink lots of water
- Reduce refined carbs intake
- Never overdo anything
- Be happy!
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email