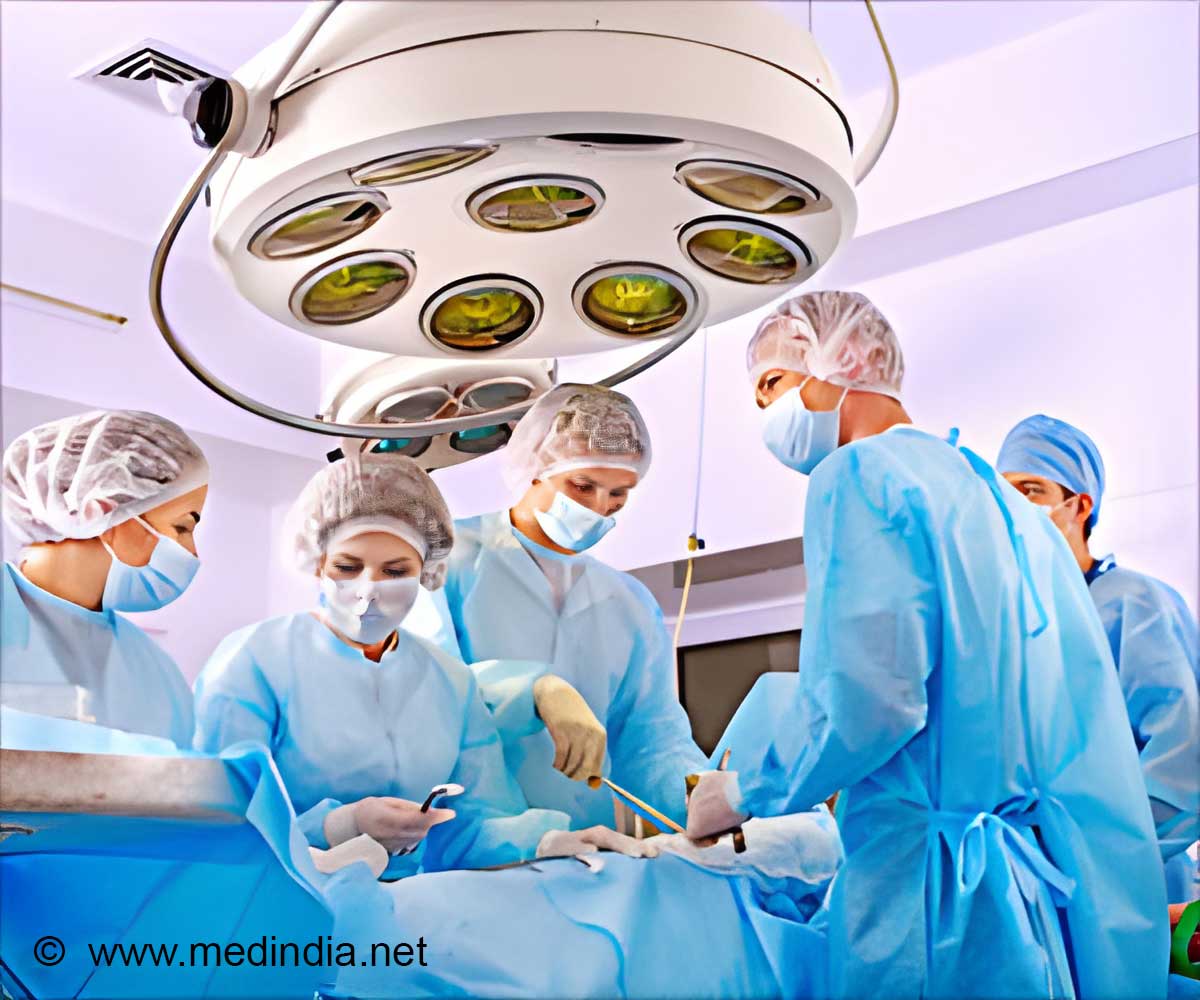
New study suggests that surgeons under stress make more mistakes in the operating room. Surgical errors mostly happen during surgery and can lead to further complications.
TOP INSIGHT
Surgeons under stress make more mistakes in the operating room. Surgical errors often happen during surgery. This can lead to further complications and sometimes even death.
The results of the study could lead to the development of protocol aiming to reduce acute or short-term stress on surgeons working in the operating room. Medical errors cause between 250,000-440,000 deaths annually in the U.S., with a proportion of those mistakes occurring in operating rooms. Any change in common practice that reduces the number of mistakes made by surgeons due to stress would also reduce the number deaths.
It's an important study published in a prestigious journal, and even more impressive is that its lead author, Peter Dupont Grantcharov, is a master's student at the Data Science Institute at Columbia University. A year and a half ago, Grantcharov had the idea to ask Dr. Homero Rivas, Associate Professor of Surgery at Stanford Medical Center, to wear a Hexoskin Smart Shirt under his scrubs while he did surgeries.
The shirt, designed to give athletes precise physiological data during workouts, measures the electrical impulses that trigger heartbeats. From this data, Grantcharov derived heart-rate variability statistics? the variation in times between heartbeats, to determine Rivas's momentary stress levels.
Grantcharov was also allowed in the operating room, where he collected laparoscopic video recordings of Rivas as he worked. Another researcher later reviewed the recordings and documented Rivas's mistakes using validated frameworks for assessing surgical performance. Both his stress levels and surgical errors were time stamped so that Grantcharov could correlate the two. This data yielded the somewhat alarming finding that the effect of short-term stress on surgical error is as high as a 66 percent increase.
"Many machines have alarms that go off periodically, equipment malfunctions, side conversations take place, people walk in and out of the OR - I could go on. My hope is that other researchers will build upon our work to make further strides in learning about the causes of stress on surgical personnel. If our study helps make the OR a safer place for patients, I'd be thrilled."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email










