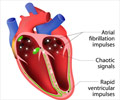
MicroRNA molecules identified in circulating blood could potentially act as biomarkers for atrial fibrillation.

TOP INSIGHT
Four miRNAs not previously associated with AF were significantly upregulated in the serum of AF patients, indicating their potential use as AF biomarkers.
A team of researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) addressed this issue by comparing miRNA expression in AF patients and healthy controls, and between control mice and those with a similar abnormal heart rhythm to AF. They showed that four miRNAs not previously associated with AF were significantly upregulated in the serum of AF patients and diseased mice, indicating their potential use as AF biomarkers. The study results were recently published in Circulation Journal.
Initially, human serum and mouse atrial tissue were screened for 733 and 672 miRNAs, respectively. These were eventually narrowed down to four by excluding non-detectable and non-specific miRNAs, and focusing on the quantification of their expression.
"One of the miRNAs, miR-214-3p, is implicated in inflammation, so we wondered whether this might be the underlying mechanism of miRNA-induced AF pathology," first author Yu Natsume says. "We compared miRNA expression with levels of a serum inflammatory factor but found no correlation suggestive of an association."
Statistical analysis of diagnostic ability showed that miR-214-3p and miR-342-5p had the highest accuracy as individual biomarkers at predicting AF, but that a combined analysis of all four miRNAs slightly improved this accuracy.
The researchers propose additional studies to determine the functional role of the identified miRNAs with respect to AF.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email