- Hemoglobin and Functions of Iron - (https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/hemoglobin-and-functions-of-iron)
- More Information On Iron Deficiency Anemia - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3280776/)
- Iron - (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/)
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia - (https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/iron-deficiency-anemia)
- About Iron-Deficiency Anemia - (https://www.hematology.org/patients/anemia/iron-deficiency.aspx)
- Individualized Treatment for Iron Deficiency Anemia in Adults - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2582401/)
Why Do We Need Iron?
Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, whose function is to transport oxygen to all parts of the body. Iron is a critical component of hemoglobin. Normally, the total amount of iron in our body is around 3-4g. About 75% of this iron is associated with hemoglobin and another muscle protein called myoglobin. The remaining 25% is stored in our body in various tissues to be released for contingencies.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hemoglobin and Functions of Iron
Go to source)
Whenever the supply of iron for the normal synthesis of hemoglobin falls, symptoms of iron deficiency anemia develop.
The normal hemoglobin value ranges from 12 to 17 grams and is slightly higher in males as compared to females. The normal reference values in the Western countries and the corresponding Indian reference ranges are as follows:
| Men (g%) | Women (g%) | |
| Western | 13.5 – 17.5 | 12 – 15.5 |
| Indian | 12.3-17 | 9.9-14.3 |
If the value of hemoglobin falls below the reference range, then the person is said to suffer from anemia.
How Much Iron Does a Woman Need?
The dietary requirements (recommended dietary allowance or RDA) of iron are higher in women than men. This requirement is further increased during pregnancy and lactation. It is important that this additional requirement is provided by iron supplements. The RDA of iron supplements for various groups is as follows:(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Iron
Go to source)
| Population group | RDA (mg) |
| Men | 10 |
| Women (14-45yrs) | 20 |
| Pregnancy | 40 |
| Lactation | 25 |
What are the Causes and Symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anemia?
In general, iron deficiency anemia is more common in women because of monthly menstrual blood loss and blood loss during childbirth.
Causes of Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Deficiency in diet
- Malabsorption states – examples include surgical removal of stomach (gastrectomy), inflammation of stomach lining (auto-immune gastritis) or gluten allergy and inflammation (gluten induced enteropathy).
- Increased demand states (especially associated with dietary deficiency) – pregnancy, growth states.

- States of chronic blood loss – abnormal bleeding from the uterus (menorrhagia), bleeding from stomach - peptic ulcer or esophageal varices, piles, colitis, diverticulitis, drug induced bleeding due to irritation of stomach lining (e.g. aspirin) and hookworm infestation.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Go to source)
Symptoms and Signs of Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Pale appearing mucous membranes of eyes and tongue.
- Severe iron deficiency can lead to brittle and spoon shaped nails (koilonychia), sores at the corners of the mouth and atrophy of the taste buds.
- Person may have difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia) due to pharyngeal web formation (Plummer – Vinson syndrome).
- Pica - wanting to eat non-food items such as mud (common in children).
- Breathlessness on exertion, fatigue, increased heart rate or palpitations and headaches.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Go to source)

What are Iron Supplements?
As mentioned, iron deficiency anemia can be treated easily. Drugs used to treat this condition are termed hematinics or iron supplements. They are administered either orally, intra-muscularly or intravenously to treat or prevent iron deficiency anemia in susceptible groups example pregnant women.
It is important to investigate thoroughly and determine the cause of iron deficiency and treat that condition too. Common examples include:
- Menstrual problems
- Gastritis
- Hookworm infestation
- Piles
- Cancer stomach or colon
In general easily dissociable ferrous salts are preferred since they are low-cost, have high iron content and are well absorbed compared to ferric salts.
The amount of elemental iron is more important than the quantity of iron per dose unit.
Sustained release preparations are expensive and not effective. In general, liquid iron preparations are less effective and may stain the teeth. If taken, they should be placed at the back of the tongue and swallowed.
Absorption is best on empty stomach, but side-effects may occur. Thus, a larger dose may be taken with meals or a smaller dose in between meals.
Parenteral Iron
Unless the deficiency is severe, the preferred route of drug administration is oral. In severe cases, when a rapid rise in hemoglobin levels is desired, iron may be administered parenterally, by intramuscular or intravenous route.
This route is also preferred in cases where the patient is unable to tolerate oral iron preparations due to side effects or malabsorption states limit absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Individualized Treatment for Iron Deficiency Anemia in Adults
Go to source)
What are the Benefits of Iron Supplements?
- Highly useful in the management of iron deficiency anemia. When the patient is responding to therapy, the hemoglobin usually rises at a rate of 0.5-1g% every week. The response is faster during early stages of treatment, when the deficiency is more severe. Treatment has to be continued for 1-3 months to achieve normal hemoglobin levels and for two to three months thereafter to replenish the iron stores.
- Necessary in patients who are administered erythropoietin (example - kidney failure), since body is unable to mobilise the sudden increased requirement of iron needed to keep with the demand of erythropoiesis.
- As dietary supplement during pregnancy and infancy. These two populations are at risk for development of iron deficiency anemia unless medicinal supplements are administered.
- Treatment of megaloblastic anemia ( due to vitamin deficiency) may unmask latent iron deficiency. Iron supplements are also useful in such patients.
What are the Side-effects of Iron Supplements?
These are common even with therapeutic doses and include:
- Nausea,
- Metallic taste,
- Epigastric (a segment in the abdomen) pain,
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea,
- Constipation is more common due to astringent action of iron.
As mentioned above, the side effects may be minimized by taking the medication with meals.
Dietary Sources of Iron
The following foods form good source of dietary iron
- Dry beans
- Dry fruits
- Yeast
- Wheat germ
- Egg yolk
- Liver
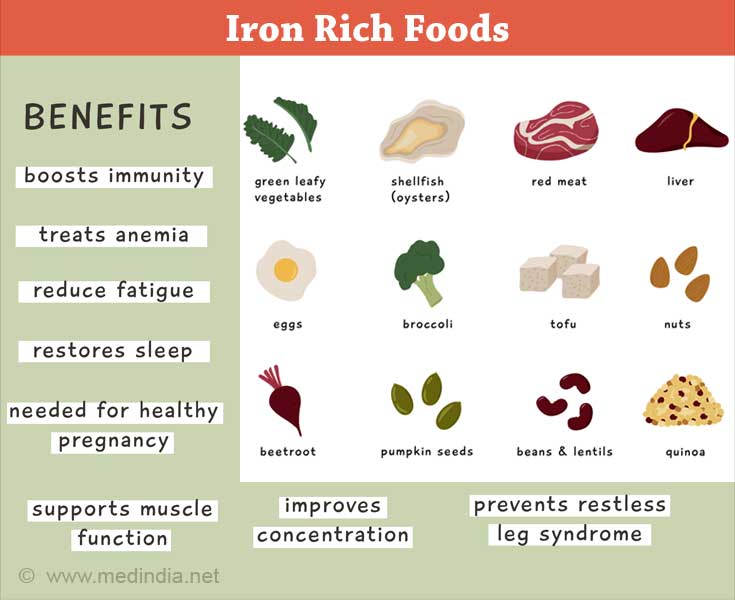
Moderately Iron rich foods
Poor Source of Iron
- Milk and milk products
- Root vegetables(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
More Information On Iron Deficiency Anemia
Go to source)
Health Tips - Prevention is better
- Necessary to eat a proper balanced diet. Vegetarians, especially should include greens at least thrice a week.
- Avoid self-medication with pain killers. Consult a doctor.
- Women, especially in childbearing age should have regular health check-ups and blood tests, at least once a year if not more.