- How To Improve Your Poor Circulation - (http://www.poorcirculation.org/)
- 10 Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation - (http://www.healthynaturalcures.org/10-warning-signs-poor-blood-circulation/)
- 5 Tips TO Improve blood circulation - (http://johnstonhealth.org/2012/03/5-tips-to-improve-blood-circulation/)
- Heart and circulatory system - (http://kidshealth.org/en/teens/heart.html)
What is Poor Circulation of Blood?
Poor blood circulation is the impaired flow of blood to certain parts of the body. It is mostly noticed at body extremities like the toes and fingers.
Poor blood circulation is a condition that results from an underlying disturbance, disorder or disease. The reduced circulation of blood occurs over a period of time. It manifests itself mostly at an older age. Years of lifestyle choices, imbalanced diet and lack of physical exercise along with some underlying conditions are some causes. These lead to fatty deposits on arterial walls. The hardened fat is called plaque which obstructs blood from flowing freely to and from the heart.
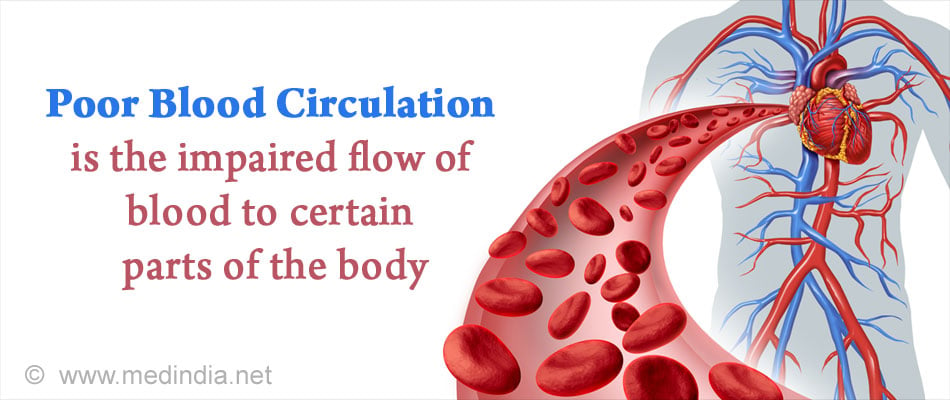
The circulatory system consists of the heart and blood vessels. The heart pumps the blood to flow through the arteries, veins and capillaries. Blood helps transportation of nutrients like electrolytes, amino acids and other substances like oxygen, carbon-dioxide, hormones and white blood cells.
Blood helps in maintaining homeostasis, i.e., the regulation of electrolytes, extra-cellular fluids, pH levels and body temperature.
Poor circulation affects the brain, heart, liver, kidneys, limbs and sex drive.
Functions of Circulatory System
- Regulation of body temperature by directing blood flow to the required parts of the body and skin.
- Communication of blood hormonal levels to trigger or stop the secretion of the required hormone.
- Defense against external particles by clotting of a wound.
- Providing immunity against pathogens by blood clots, white blood cells and distribution of antibodies
- Absorption of nutrition from the linings of the intestinal walls.
- Transportation of the following:
- Oxygen – Hemoglobin binds with oxygen taken from the lungs and transports it to the various tissues and muscles in the body.
- Nutrients – Various nutrients like vitamins, minerals, glucose, lipids, amino acids are transported by blood.
- Waste from cells – Waste substances like urea, carbon-dioxide and other substances are taken away when the blood takes them through the kidney cells.
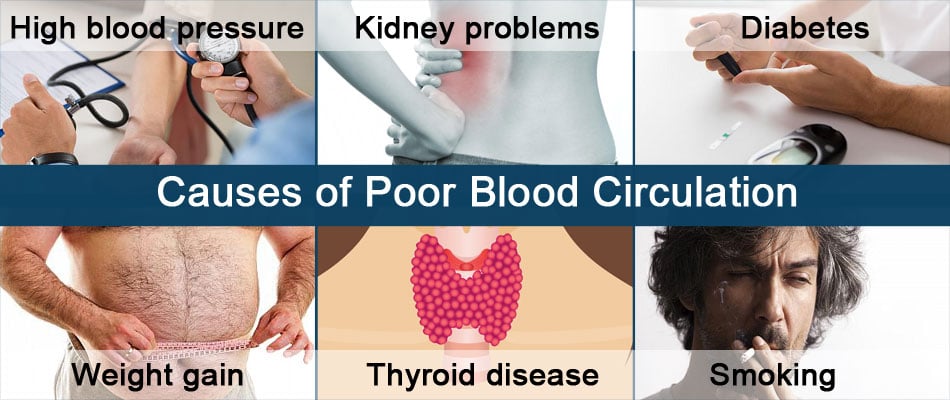
What are the Causes of Poor Blood Circulation?
- Plaque build-up in the blood
- Fat build-up on the inner walls of the blood vessels
- Embolism or thrombosis that blocks the blood vessels
- High blood pressure
- Heart malfunctions
- Kidney problems
- Peripheral artery disease
- Poor diet
- Diabetes
- Weight gain
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Thyroid disease
- Anemia
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Emphysema
What are the Warning Signs of Poor Blood Circulation?
Warning signs of poor blood circulation can be both physical and mental, especially since the blood circulation affects the brain. The symptoms of poor blood circulation depend on the area affected.
Symptoms of brain:
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Memory loss
- Unexplained headaches

- Decreased cognitive ability
Symptoms of heart:
- Breathlessness on simple aerobic activities
- Chest pain
- Irregular heart beats
- High blood pressure
- Frequent exhaustion
Symptoms of liver and digestive system:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Lack of appetite
- Unexplained digestive problems
Symptoms of kidneys:
- Edema of hands, feet and ankles
- Fatigue

- Rise in blood pressure
Symptoms of extremities:
- Itchy skin on Hands, legs and feet
- Finger tips and toe tips become bluish or reddish
- Varicose veins
- Foot ulcers
- Cold hands and feet
- Numbness, tingling or stinging of extremities
- Cramping in legs, buttocks or feet
Other symptoms include:
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Weakened immunity system
- Slow healing of infections, wounds and skin injuries
- Poor judgment of pain and temperature
- Lack of stamina
- Reduced libido
- Dark circles under the eyes
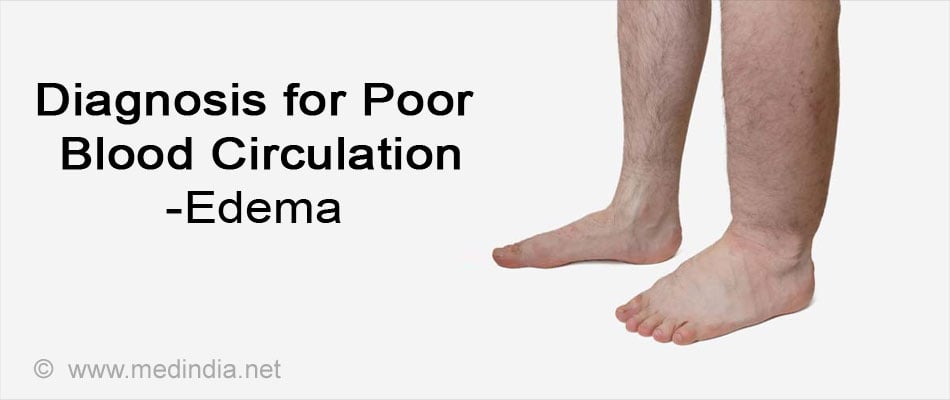
What is the Diagnosis for Poor Blood Circulation?
Diagnosis of poor blood circulation calls for history of the problem, physical exam and some clinical tests to confirm the reason for poor blood circulation in a particular area.
History:
- Family history
- History of existing problems like dizziness, memory loss, or other symptoms.
- Lifestyle of the individual.
Physical exam:
- Check for any pain, swelling or itching skin
- Bluish coloring of the extremities (cyanosis)
- Wounds that do not heal easily
- Edema of hands and legs
Diagnostic tests:
Based on the history and physical exam, doctor may suspect an underlying disease. The diagnostic tests prescribed depend on the kind of underlying disease. Some tests that help in understanding the blood circulation in a particular area of the body include:
- Blood pressure measurement
- Ultrasound
- Doppler test
- Arteriography
- Sphygmomanometer
- Imaging studies like MRI or CT scan
- CT angiogram
- Angiography
How do you Improve Poor Blood Circulation?
Poor blood circulation can be caused by various factors. Tackling those factors can improve blood circulation:
General changes in lifestyle like dietary changes and being more active can help in improving blood circulation. The treatment of underlying conditions that cause the poor blood circulation are mostly related to lifestyle diseases like heart conditions and diabetes.
Some specific remedies for poor blood circulation are as follows:
Symptomatic:
- Compression socks for swollen legs
- Pain relievers
- Heparinoid creams
- Physical therapy
- Hydrotherapy
- Aerobic exercise
- Body massage or massage to the affected areas like limbs
Dietary changes:
- Vitamins like B6 and B12, niacin, Vitamin E, Vitamin C and magnesium
- Flavonoids as found in dark chocolate
- Cut on alcohol and smoking
- Avoid caffeine related products like coffee and tea.
- Garlic is a natural blood thinner
- Cayenne pepper improves metabolic rate and blood circulation
- Fish – Omega 3 fats
- Watermelons are rich in lycopene that eases the blood flow
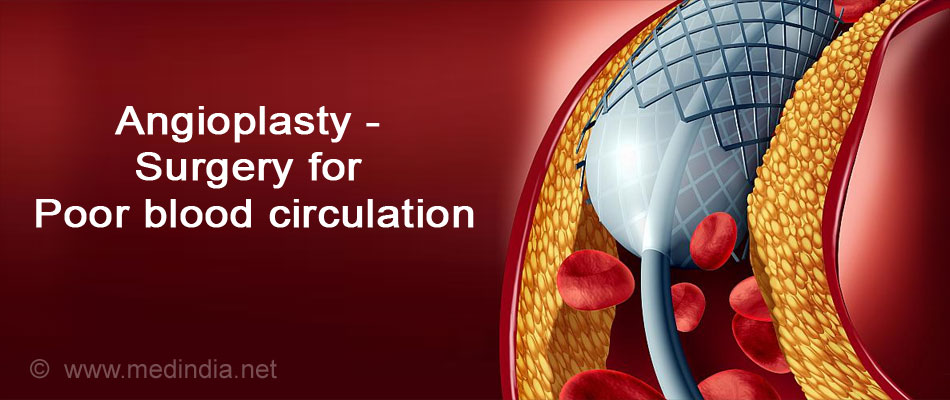
Surgery:
Surgery is one of the last options for severely affected people.
- Angioplasty and stent – Widens obstructed or narrowed arteries or veins with minimally invasive surgery.
- Atherectomy: Surgery done inside blood vessels to remove atherosclerosis from the blood vessels.
- Revascularization: Restoration of blood flow to the part of the organ or body that has not been receiving blood supply (ischemia).
- Endarterectomy: Surgical removal of the obstructed part of the artery and resume the blood flow.
- Surgical treatment for conditions like varicose veins.
Health Tips
- Drink plenty of water, apart from other fluids.
- Keep the muscles moving with active lifestyle.
- Take warm bath and shower if you have cramps.
- Reduce stress levels.
- Quit smoking and avoid alcohols.
- Correct your posture, while standing and sitting.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email






