- Pharmacological characteristics of metamizole - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24724493/ )
- Metamizole-Associated Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4405027/ )
- Real world evidence of the use of metamizole (dipyrone) by the Brazilian population. A retrospective cohort with over 380,000 patients - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9060643/ )
- Metamizole (Dipyrone) as an Alternative Agent in Postoperative Analgesia in Patients with Contraindications for Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27346584/)
Metamizole Medication Information
Discover comprehensive details about Metamizole, including its pronunciation, uses, dosage instructions, indications, and guidelines on how and when to take it or avoid it.
The updated prescription information covers potential side effects, precautions, warnings, and storage recommendations.
Additionally, explore the Metamizole brands available in India and internationally, along with pricing information. For personalized advice, consult your healthcare provider.
Generic Name : Metamizole Pronunciation : Met-ami-zole Therapeutic Classification : Analgesic And Antipyretic AgentBrand Names or Trade Names of Metamizole
India :
Overview of Metamizole
• Metamizole is also known as dipyrone.• It has analgesic properties.
• Metamizole is used for the treatment of postoperative pain and other painful conditions.
Why is Metamizole Prescribed? (Indications)
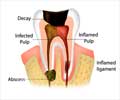
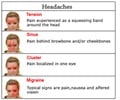
Metamizole is a painkiller used for the treatment of fever, headache, toothache, postoperative pain and other painful conditions.It belongs to the group non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
It has been banned in several countries including the United States and India due to its ability to reduce white blood cell counts and cause a condition called agranulocytosis.
When should Metamizole not be taken? (Contraindications)
Metamizole should not be used by patients with:• Allergy to the drug or other NSAIDs
• Liver or kidney problems
• Low blood counts
• Stomach ulcer
• Acute intermittent porphyria
• Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
• Asthma, optic neuritis, myasthenia gravis, glaucoma, enlarged prostate
It should also not be used during pregnancy, breastfeeding and in children and the elderly.
What is the dosage of Metamizole?
• The recommended oral adult dose for metamizole is 500 mg 3-4 times up to a maximum dose of 4000 mg/day.• The injection is administered in a dose of 250-500 mg three times a day up to a maximum daily dose of 2g in adults into a muscle or a vein.
How should Metamizole be taken?
• The tablet should be administered orally with food.• The intravenous dose should be administered through a slow infusion into a vein.
What are the warnings and precautions for Metamizole?
• The higher dose levels may be dangerous for patients.• • Doctors should monitor the blood count at the time of treatment.
• Patients with low blood pressure should not use this drug. The intravenous drug should not be given rapidly since it can cause a fall in blood pressure.
What are the side effects of Metamizole?
Blood: Reduced white blood cell counts (agranulocytosis), reduced red blood cell counts due to reduced production of the cells (aplastic anemia). May trigger acute porphyriaSkin: Severe skin reactions like toxic epidermal necrolysis
Kidney: Kidney damage
Cardiovascular system: Low blood pressure
Others: Allergic reaction which may include a rash, low blood pressure, and breathing difficulty
What are the other precautions for Metamizole?
• Patients allergic to soy or peanut should not take the medication.• It should not be taken with alcohol.
What are the Drug Interactions of Metamizole?
• Metamizole may increase the effect of anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs.• It may interact with anti-hypertensive drugs causing low blood pressure.
• It may alter the effects of penicillin, sulfonamides, corticosteroids and anti-diabetes drugs.
• It may reduce the effect of cyclosporine.
• Sedatives and hypnotics may increase the blood levels of metamizole.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email