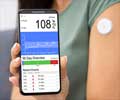
Why should one check the blood glucose?
Tight blood glucose control reduces the risk and delays the onset of diabetes-related complications.
A number of studies have emphasized that regular and consistent self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) should be a part of all diabetes management programs. Tight blood glucose control reduces the risk and delays the onset of diabetes-related complications like retinopathy, neuropathy, heart attack, and nephropathy besides benefiting the patient immensely.
Most people with diabetes are under the impression that once the doctor has adjusted the medication, the blood glucose levels remains unaltered for few months. This, however, is not the case as there are many variables that affect the blood glucose levels by the minute. However, the normal physiology of the body keeps these fluctuations within a narrow band. The various factors that cause these fluctuations are as follows:
Food: It is not possible for one to eat the same type and amount of food all the time. Food has various components and carbohydrates are primarily responsible for the variation in the blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates present in the food get converted to glucose. The rate at which this conversion takes place depends on the particle size as well as the presence/absence of other components, i.e., fruit juice raises the blood glucose much faster than eating a fruit. This is because the former is devoid of fiber - the component that keeps blood glucose down. Similarly the presence of protein with a carbohydrate in diet raises the blood glucose level slower than only when carbohydrates are present.
Insulin: In a non-diabetic person, insulin is released in the body in the presence of food i.e carbohydrate. This keeps the blood glucose level under control. In a person with diabetes where there is either less insulin secreted or the cells are resistant to insulin, injections are required. The timing and quantity of the insulin injections must be adjusted in a way that at any given time the blood glucose is neither too high nor too low. The amount of insulin absorbed by the human body after it is injected can vary as much as 25% from day to day. This has been attributed to various reasons like -
- Site of insulin injection - If the same site is used for daily injections the rate of absorption is less.
- If insulin is injected in the abdomen, the rate of absorption is faster than if injected in the thigh.
- The amount of insulin absorbed is also dependent upon the physical activity performed by that part of the body where the insulin is injected. For example, if insulin is injected in the arm after strenuous exercise involving the arm - the rate of utilization of insulin will be quite high.
- Exercise: During exercise, the muscles, which are working, have to use the glucose as fuel and this brings down the glucose levels in the body. Exercise also increases the insulin sensitivity especially in the muscles, i.e., less insulin is required to push glucose into the cell. On a day when there is less or no exercise there may be an increased requirement of insulin and hence there is variation in the blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Over time this is perhaps one of the most important factors and may have been responsible for recent increase in the incidence of diabetes and heart diseases in the world. To effectively cope with stress certain hormones are released that keep the blood glucose levels high. The dynamics of current lifestyle changes constantly and so it is with stress. People react differently to stress depending on their personality types. Some people may be more susceptible to the physical harms of stress than others. There are also examples of people who eat more and some who eat less when faced with a stressful situation. One cannot quantify stress and proportionate it in terms of knowing how much of it can raise the blood glucose; however, people who lead a stressful life are known to be more prone to diabetes and heart disease.
- Illness or Infections: These can bring about tremendous variation in the blood glucose levels. Since the body is under stress during an illness, certain hormones are produced which are counterproductive to the action of insulin. This can raise the blood glucose levels. Over-the-counter medications are also taken during illness by some individuals. Some of these medicines especially those containing alcohol or sugars can raise the blood glucose levels.
We eat too much, drink too much, smoke too much, drive too fast, and walk too little. - Margaret C. Heagarty, 1976