- Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, 12th edition - (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299345706_Carranza's_Clinical_Periodontology_12th_edition)
- Hereditary gingival fibromatosis and growth retardation - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11585376/)
- Amlodipine-induced Gingival Hyperplasia – A Case Report and Review - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4763906/)
- An unusual case of generalized severe gingival enlargement during pregnancy - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21062713/)
- Hereditary gingival fibromatosis: a systematic review - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16671866/)
- Central regulation of blood eosinophilia by the beta-adrenergic system in rats - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2558)
- Idiopathic gingival hyperplasia: clinical features and differential diagnosis - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22129779/)
- Cyclosporin-induced gingival overgrowth in a child treated with CO2 laser surgery: a case report - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12597682/)
What is Gingival Hyperplasia?
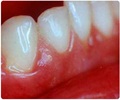
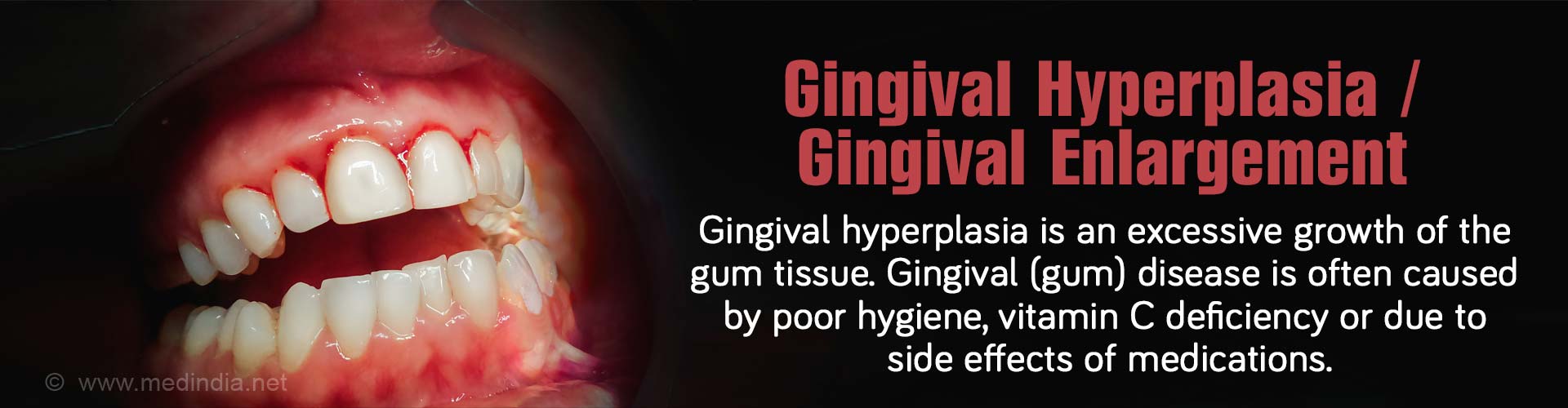
Gingival hyperplasia is when gums grow too much around teeth because there are too many gum cells. This makes the gums get bigger and it's a common problem in gum diseases. People also call it gingival overgrowth or hypertrophic gingivitis.
Other names for gingival hyperplasia includes gum hypertrophy, gingival hypertrophy, gum hyperplasia, gum swelling and idiopathic gingival enlargement.
Its classification, grading, and differential diagnosis play significant roles in effective management. It helps in distinguishing it from other causes of gingival swelling or inflammatory gingival enlargement(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, 12th edition
Go to source).
What are the Causes of Gingival Hyperplasia?
Swelling
: Gums can get big and red when they're irritated. This irritation can be due to bacteria on teeth, not cleaning well, dental work, gum problems, or infections. Keeping teeth clean by brushing and flossing can help.Medications
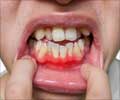
: Certain drugs can trigger gingival hyperplasia, with phenytoin being a notable example. The enlarged gums are usually firm and light pink, not easily bleeding or painful. This can occur with medicines for seizures, weakening the immune system, or high blood pressure. Upon discontinuing the medication, a reduction in gum growth typically ensues.Systemic Conditions
: It can also be linked to specific systemic conditions. This includes leukemic gingival enlargement or during pregnancy.Genetic Predisposition
: Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) and neurofibromatosis are rare hereditary conditions that develop during childhood. In this, excessive production of collagen, a type of protein found in the gums, causes the gingival overgrowth in this condition. The enlarged gums may cover major part of the tooth surface or the entire tooth surface(2✔ ✔Trusted SourceHereditary gingival fibromatosis and growth retardation
Go to source, 3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Amlodipine-induced Gingival Hyperplasia – A Case Report and Review
Go to source).
Other Causes Include:
- Vitamin C deficiency
Smoking - Overcrowded teeth
Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy and puberty
: Hormone changes in pregnancy and puberty can cause gums to grow too much. But after fixing the main issue, like having the baby, the gum growth usually gets better(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
An unusual case of generalized severe gingival enlargement during pregnancy
Go to source).

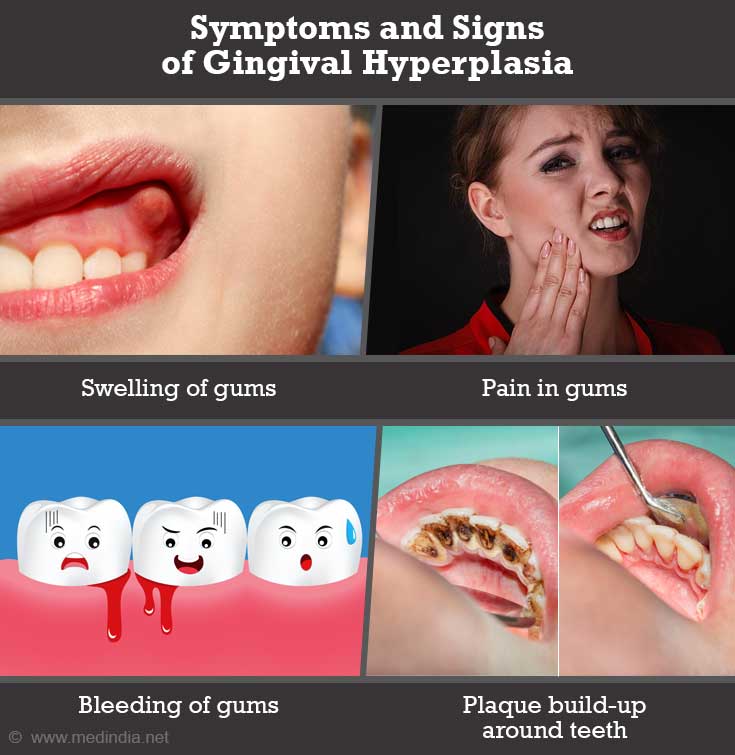
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Gingival Hyperplasia?
The visible signs and symptoms of gingival hyperplasia include -
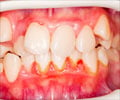
- Swelling of the gums
- Pain and discomfort in and around gums
- Redness and bleeding of gums
- Infection and pus formation
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth that may fall
- Plaque build-up on the teeth and bleeding
- Gum enlargement may interfere with chewing or speech
- Looks unsightly and may lead to psychological problems.
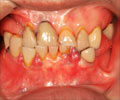
In more severe cases, the gums can completely cover the teeth and can affect alignment of teeth, it also makes it hard to clean, which raises the chance of getting gum disease.
When gingival overgrowth occurs during childhood, it affects the overall tooth eruption process.
Gingival Enlargement Classification
Gingival enlargement can be classified into different types based on its underlying causes and characteristics. These classifications help in better understanding the condition and determining appropriate management strategies. The main types of gingival enlargement include:
Drug-Induced Gingival Enlargement
: Caused by certain medications, leading to overgrowth of gum tissues.Hereditary Gingival Fibromatosis
: A genetic condition causing progressive and excessive gum growth.Inflammatory Gingival Enlargement
: Resulting from inflammation due to factors like poor oral hygiene or gum diseases.Idiopathic Gingival Enlargement
: Enlargement with an unknown cause, often seen in certain genetic or systemic conditions.Neoplastic Gingival Enlargement
: Linked to tumors or abnormal growths on the gums, which can be benign or malignant.False Gingival Enlargement
: Occurs due to factors other than true tissue growth, like excessive gum inflammation or swelling.
Each classification helps guide diagnosis and treatment approaches for managing gingival enlargement effectively.
How is Gingival Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Dentists usually figure out if your gums are too big by talking to you and looking in your mouth. Sometimes, they might need extra tests like blood tests or checking a small piece of gum, but that's not common.
Gingival Hyperplasia Histopathology
: The condition can be confirmed through histopathology. This involves examining gum tissue (gingival tissue) under a microscope. Microscopic examination of the gums shows an abnormal proliferation of gums cells(5✔ ✔Trusted SourceHereditary gingival fibromatosis: a systematic review
Go to source).
Gingival Enlargement Grading
: It requires evaluating the seriousness of excessive gum growth. Dentists utilize this grading scheme to gauge the degree of gum enlargement and to direct suitable treatment choices. This procedure aids in categorizing the condition and customizing interventions depending on the level of gingival overgrowth seen in individual(6✔ ✔Trusted SourceCentral regulation of blood eosinophilia by the beta-adrenergic system in rats
Go to source, 7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Idiopathic gingival hyperplasia: clinical features and differential diagnosis
Go to source).
Gingival Enlargement Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of gingival hyperplasia involves distinguishing it from other conditions that might show similar symptoms or features. Some potential conditions that can resemble gingival hyperplasia include:
Gingivitis
: Inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding.Gingival Fibromatosis
: A genetic condition characterized by firm, fibrous gum tissue that progressively enlarges.Pyogenic Granuloma
: A non-cancerous growth on the gums, often resulting from irritation or trauma.Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
: A reactive lesion that forms on the gums or oral tissues, usually as a result of injury.Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
: A benign growth on the gums containing both gum and bone-like tissue.Leukemia-Associated Gingival Enlargement
: Enlargement of gums due to underlying leukemia, often associated with bleeding and discoloration.Drug-Induced Gingival Enlargement
: Overgrowth of gums triggered by certain medications.Pregnancy-Induced Gingival Enlargement
: Temporary enlargement of gums during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.Idiopathic Gingival Enlargement
: Gum enlargement with no identifiable cause.Fibroma
: A benign tumor composed of connective tissue, which can occur in the oral cavity, including the gums.
A proper differential diagnosis is crucial for accurate treatment and management of gingival hyperplasia. It also addresses any underlying conditions that might contribute to the symptoms.
How is Gingival Hyperplasia Treated?
Treatment of gingival hyperplasia often depends on the underlying cause.
- In most cases improved oral hygiene can prevent or reduce severity of symptoms.
- If the reason is swollen gums, then brushing and flossing well to remove germscan often make the gums better.
- Use of antiseptic mouthwash or a course of antibiotics to treat the oral infection are helpful.
- Yet, if the gums grow too much because of medicine, you should stop taking the drug.
- Doctors may recommend gingivectomy (surgical removal of overgrown gum tissue) for severe cases. Surgical procedures include laser excision and periodontal flap surgery(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Cyclosporin-induced gingival overgrowth in a child treated with CO2 laser surgery: a case report
Go to source). - Sometimes, people use mouthguard-like devices to slow down how fast the gum tissue grows.
- Treating the main issue is crucial. If not, the gum growth comes back, and you might need surgery again.
Gingival hyperplasia treatment at home: While professional treatment is important, there is growing interest in home remedies for managing gingival hyperplasia. Approach these with caution.

How to Prevent Gingival Hyperplasia?
- Good oral hygiene - Brush teeth after meals to remove residue sticking to the gums. Maintain good oral hygiene measures and visit your dentist for regular dental checkups.
- If the gum growth is because of medication, talk to your doctor and consider stopping or changing the medication.
- Eating sugary foods can make gum growth worse, so it's best to limit or avoid them.Children are most affected since they consume more sticky sweets and usually do not take proper care of their teeth. So, it's a good idea to watch over children while they clean their teeth to make sure they're doing it properly.
- Some natural things like eucalyptus oil, cloves, green tea, and more can help at first. Also, eating foods rich in vitamin C, like fruits and vegetables, can keep gums healthy.
To conclude, chronic inflammatory conditions can often lead to gingival hyperplasia. It is a visible oral manifestation characterized by swollen gums and excessive growth of gum tissue.
When diagnosing this condition, it's crucial to consider a differential diagnosis. This is to rule out other potential causes such as drug-induced gingival overgrowth. In some cases, gingival fibroblasts, specialized cells in gum tissue, play a role in the overgrowth.
Treatment strategies vary depending on the cause, ranging from improved oral hygiene practices. They include methods like brushing and flossing. It also includes advanced interventions such as scaling and root planing or even surgical removal of the excess gum tissue.
Calcium channel blockers, often used to treat high blood pressure, can sometimes induce gingival enlargement as a side effect. A comprehensive dental cleaning and maintenance regimen can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and hyperplasia.
Interestingly, similar oral manifestations, such as gingival hyperplasia. This has also been observed in dogs (Hyperplasia in dogs). To address this condition effectively, thorough case reports and studies are essential to understand its mechanisms and develop appropriate treatment protocols.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email