Pain killers like diclofenac sodium may lead to severe allergic reactions and heart attack in Kounis syndrome or allergic acute coronary syndrome.
- Allergic reaction (Type 1 hypersensitivity reactions) and heart attack (acute coronary syndromes) may be triggered by several drugs in Kounis syndrome condition
- Kounis syndrome or acute coronary syndrome is caused by allergic reaction to a drug or substance
- Diclofenac sodium – a widely used NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) may stimulate allergic reactions, including heart failure at an incidence, higher than reported
- It is henceforth suggested that heart attack risk due to allergic reactions to these drugs must be kept in mind when prescribing
Read More..
Although the definite prevalence of the syndrome is not known, it may cause serious life-threatening cardiovascular events. There are two reported variants of this syndrome leading to heart attack, that occur as a result of vasoactive and inflammatory mediators due to hypersensitivity reaction:
- Type 1 – Vasospasm occurring in normal coronary arteries
- Type 2 – Atherosclerotic plaque rupture
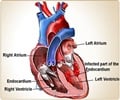
Drug-Induced Heart Attack in Kounis Syndrome
The case report demonstrates the event of Type 2 Kounis syndrome that leads to acute anterior myocardial infarction (heart attack) followed by cardiac arrest (heart attack, heart failure). A healthy 49-year-old male was reported to develop the syndrome soon after intramuscular injection of diclofenac sodium.Diclofenac sodium is a broadly used NSAID that may provoke allergic reactions, including heart failure in the present case. Earlier studies have also mentioned the effects of diclofenac in ACS.
The equivalence between two molecules, thromboxane A2 (vasoconstrictor) and prostacyclin (vasodilator) is essential for the control of normal circulation. As the NSAIDs alter this balance between thromboxane-prostacyclin equilibrium, it causes vasospasm (narrowing of the blood vessels – arteries) followed by the development of small platelet thrombi (blood clot). Thus, the anti-prostacyclin effects are the adverse reaction of NSAIDs.
Another supportive clinical feature apart from the abrupt onset of heart attack in Kounis syndrome is high levels of IgE (immunoglobulins E, a type of antibody)
Risks and Side Effects of NSAIDs
The risk factors include:- People over 65 years old
- Pregnancy/breastfeeding
- Asthma
- Allergic reactions to NSAIDs
- Heart, liver, kidney ailments
- Hypertension and/or diabetes
- Stomach pain/ stomach ulcers
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
References:
- Kounis syndrome triggered by diclofenac sodium injection which leads to myocardial infarction and cardiac arrest: Caglar EmreCagliyan et al: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jccase.2013.03.002
- Interrelationships between prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 - ( https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6258879/)
- Allergic acute coronary syndrome (Kounis syndrome) - ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462222/)
- Kounis syndrome: an update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic management - ( https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26966931/)
Source-Medindia