Signs and Symptoms
When the process of cell death starts in brain due to insufficient supply of oxygen, body starts throwing alarming signals. Different sections of the brain control different functions of the body. Both, right and left, sides are controlled by the two segments of the brain. The signals are prominent on the side of the body which is controlled by the affected segment of the brain. Some of the most common symptoms of stroke are:
- Sudden mental confusion
- Trouble in speaking
- Not able to articulate words
- Trouble in visualizing from one or both the eyes
- Trouble walking
- Dizziness
- Loss of balance
- Severe headache
- Double vision
- Drowsiness
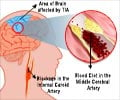
The impact of stroke differs from person to person. Some experience mild symptoms while other face severe. Signs of ischemic stroke caused by blocking of blood vessel usually occur suddenly, and signs of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bursting of blood vessel usually develop gradually. If the stroke occurs towards the backside of the brain, it is likely to affect the vision. When stroke occurs in the brain stem, it is likely to affect both sides of the body and might leave someone in a ‘locked-in’ state where the patient generally loses the ability to speak or do any movement below the neck region.
In transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), one or more symptoms occur suddenly but last only for few minutes, and then gradually subside. This attack of stroke is called "mini-strokes". Immediate medical attention reduces the risk for further brain damage and acts as a warning sign to take necessary steps to avoid a major attack.
A stroke in the right hemisphere can cause:
- Paralysis of the left side of the body.
- Problems in judging distance
- Impaired spatial and perceptual abilities.
- Increased impulsiveness in behavior
- Impaired vision
- Short-term memory loss
Stroke in the left hemisphere of the brain can cause:
- Paralysis of the right side of the body.
- Speech and language problems
- Impaired writing and reading abilities
- Slow behavior
The common symptoms include:
- Trouble speaking or understanding
- Blurred vision
- Trouble standing or walking
- Dizziness
- Slurred speech
- Numbness or paralysis of one side of the body
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Loss of consciousness or fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden face, chest and/or limb pain
- Sudden hiccups
- Seizure
- Racing heartbeat
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulties controlling the bladder and bowel right after stroke
- Mood swings