Sniffing or licking female dogs’ genitalia- a common site of Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor (CTVT) can spread this unusual cancer to the nose and mouth of male dogs.
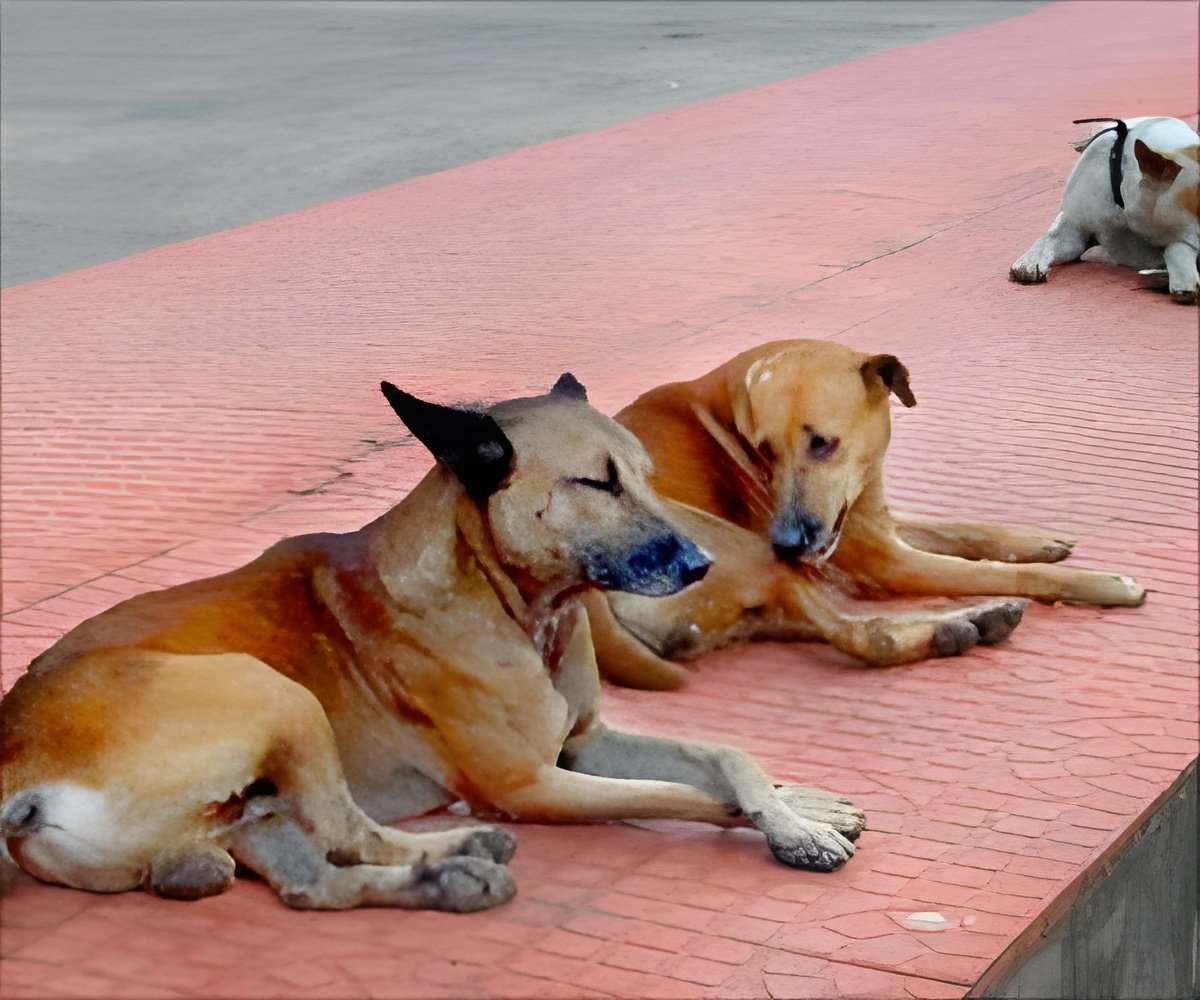

Researchers think this is because of behavior differences between the sexes: male dogs spend more time sniffing and licking female dogs’ genitalia than vice versa.
TOP INSIGHT
Sniffing or licking female dogs’ genitalia which is the common site of Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor (CTVT) can spread this unusual cancer to the nose and mouth of male dogs.
Read More..
What is Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor (CTVT)?
Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor, or CTVT, is an unusual cancer – it is infectious and can spread between dogs when they come into contact. The living cancer cells physically ‘transplant’ themselves from one animal to the other.CTVT commonly affects dogs’ genitals and is usually transmitted during mating. But sometimes the cancer can affect other areas like the nose, mouth and skin.
In the study, researchers reviewed a database of almost 2,000 cases of CTVT from around the globe and found that only 32 CTVT tumors affected the nose or mouth. Of these, 27 cases were in male dogs.
“We found that a very significant proportion of the nose or mouth tumors of canine transmissible cancer were in male dogs,” said Dr Andrea Strakova in the University of Cambridge’s Department of Veterinary Medicine, first author of the paper. She performed this study with colleagues from the Transmissible Cancer Group, led by Professor Elizabeth Murchison.
Why are Male Dogs Four Times More Likely to Develop Oro-nasal Tumors than Females?
Strakova added: “We think this is because male dogs may have a preference for sniffing or licking the female genitalia, compared to vice versa. The female genital tumors may also be more accessible for sniffing and licking, compared to the male genital tumors.”The findings are published today in the journal Veterinary Record.
CTVT first arose several thousand years ago from the cells of one individual dog; remarkably, the cancer survived beyond the death of this original dog by spreading to new dogs. This transmissible cancer is now found in dog populations worldwide, and is the oldest and most prolific cancer lineage known in nature.
CTVT isn’t common in the UK, although case numbers have risen in the past decade. This is thought to be linked to the import of dogs from abroad. The disease occurs worldwide but is mostly linked to countries with free-roaming dog populations.
“Although canine transmissible cancer can be diagnosed and treated fairly easily, veterinarians in the UK may not be familiar with the signs of the disease because it is very rare here,” said Strakova.
She added: “We think it’s important to consider CTVT as a possible diagnosis for oro-nasal tumors in dogs. Treatment is very effective, using single agent Vincristine chemotherapy, and the vast majority of dogs recover.”
Symptoms of the Oro-nasal Form of the Cancer
The most common symptoms of the oro-nasal form of the cancer are sneezing, snoring, difficulty breathing, nasal deformation or bloody and other discharge from the nose or mouth.Genital cases of CTVT occur in roughly equal numbers of male and female dogs.
Transmissible cancers are also found in Tasmanian Devils, and in marine bivalves like mussels and clams. The researchers say that studying this unusual long-lived cancer could also be helpful in understanding how human cancers work.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email