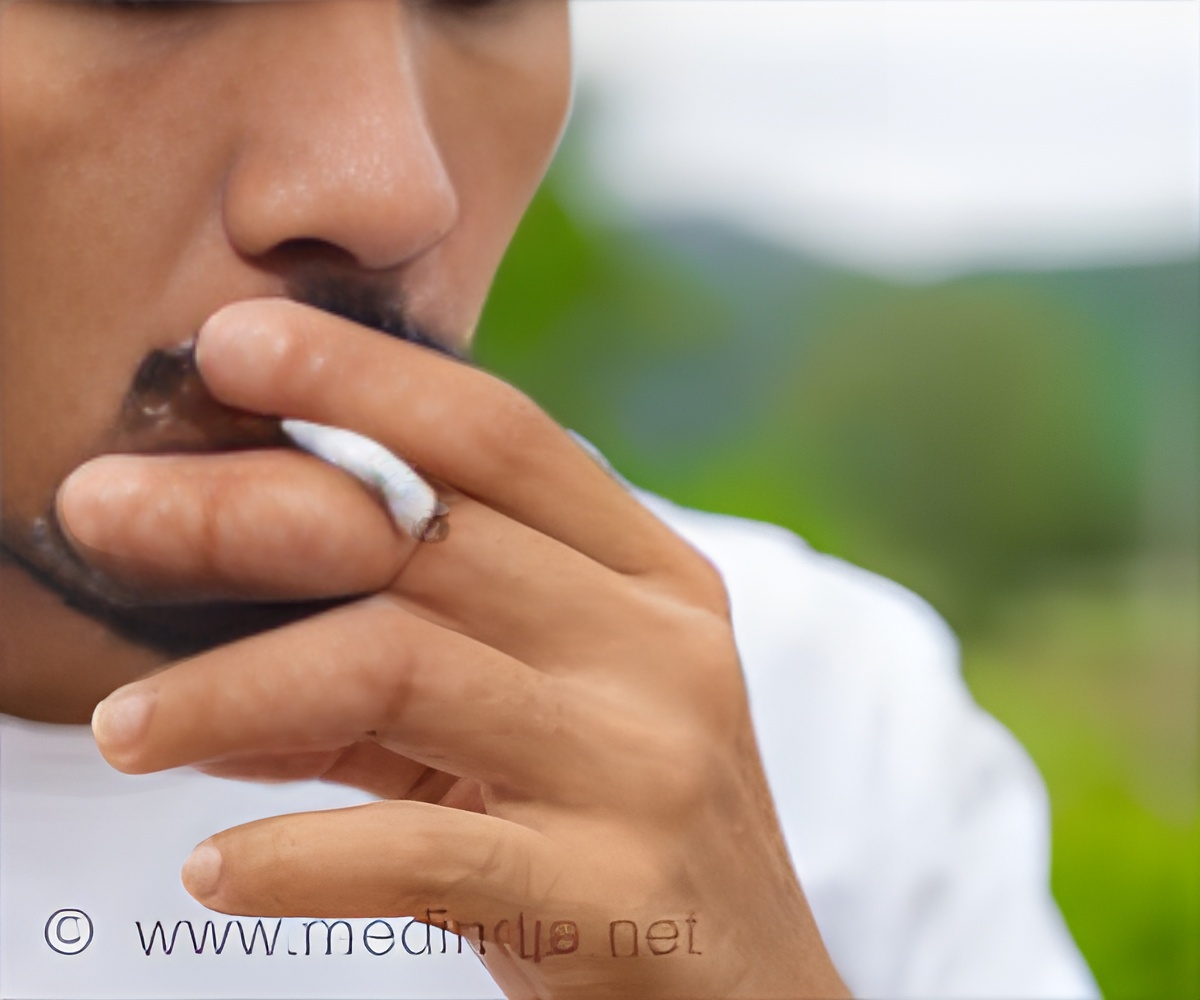
A new study contributes to a more complete picture of the association between smoking and the risk of death from prostate cancer.

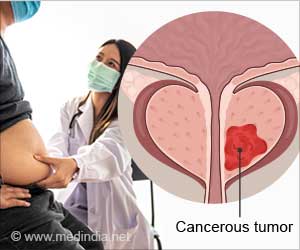
Does Smoking Worsen Prostate Cancer?
TOP INSIGHT
Smoking doesn't seem to raise the risk of prostate cancer but it increased the severity and the risk of dying from prostate cancer.
The researchers followed more than 350 000 people over several decades, and the results are now published in European Urology.
They used five Swedish population studies with self-reported information on men’s smoking habits. In total, more than 350 000 men were included in the study from 1974 and onwards.
They were then followed over the years using several national registers. The National Prostate Cancer Registry contributed data on tumor type at diagnosis, cause of detection via symptoms, or a PSA test without forthcoming symptoms (asymptomatic PSA test) and treatment.
During the period covered by the research, 24 731 of the participants developed prostate cancer and 4 322 died as a result of the disease.
A probable explanation for the lower risk of prostate cancer in smokers is that they may be less likely to take an asymptomatic PSA test.
The risk was about 20% higher among smokers than among men who had never smoked. The risk increased further if smokers were also overweight (BMI 25-30) or obese (BMI over 30).
Researchers say it is now important to identify the reason why smokers have a poorer prognosis once they have developed prostate cancer. More understanding about whether it is smoking or other risk factors, such as socio-demographic factors, that cause this association.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email


![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA]](https://www.medindia.net/images/common/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)