Drugs used for controlling cholesterol called statins could be helpful in preventing a deadly type of brain stroke.
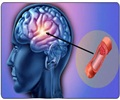
- Bleeding into the brain tissue is the most fatal type of brain stroke having a 40% to 50% mortality rate within 30 days
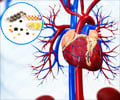
- Statins, which are drugs used for lowering cholesterol have been shown to decrease the risk of this type of brain stroke especially if taken for a long time, says a new study
- Use of statins for more than 5 years lowers the risk of brain stroke by 33% and 38% in the lobe and non-lobe of the brain respectively
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Go to source).
Cholesterol-Lowering Medicines
Go to source).
Research shows that while statins have been shown to reduce the risk of stroke from blood clots, there has been conflicting research on whether statin use increases or decreases the risk of a person having a first intracerebral hemorrhage.
Statins and Intracerebral Hemorrhage
In the recent study, researchers looked at the lobe and non-lobe areas of the brain to see if location was a factor for statin use and the risk of a first intracerebral hemorrhage and found that those who used a statin had a lower risk of this type of bleeding stroke in both areas of the brain. The risk was even lower with long-term statin use (3✔ ✔Trusted SourceCholesterol-lowering drugs linked to lower risk of bleeding stroke
Go to source).
The lobe area of the brain includes most of the cerebrum, including the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The non-lobe area primarily includes the basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellum, and brainstem.
For the study, researchers looked at health records in Denmark and identified 989 people with an average age of 76 who had an intracerebral hemorrhage in the lobe area of the brain. They were compared to 39,500 people who did not have this type of stroke and were similar in age, gender, and other factors.
They also looked at 1,175 people with an average age of 75 who had an intracerebral hemorrhage in the non-lobe parts of the brain. They were compared to 46,755 people who did not have this type of stroke and were similar in age, gender, and other factors.
After adjusting for factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and alcohol use, researchers found that people currently using statins had a 17% lower risk of having a stroke in the lobe areas of the brain and a 16% lower risk of stroke in the non-lobe areas of the brain.
This is good news for people taking statins, especially long-term because of its ability to reduce the risk of bleeding stroke as well as the risk of stroke from blood clots.
Even though the study gives promising results, it was only conducted in the Danish population. It is important to conduct similar research in other populations.
References:
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage - (https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Intracerebral-Hemorrhage)
- Cholesterol-Lowering Medicines - (https://www.cdc.gov/cholesterol/treating_cholesterol.htm)
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs linked to lower risk of bleeding stroke - (https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/12/221207163034.htm)
Source-Medindia