The recurrently demanded test in medicine is the blood test to evaluate vitamin D deficiency.
Researchers used the two new test kits on the specimens, and compared results with findings from a gold standard method called LCMS, which has been shown to provide accurate vitamin D measurements. (LCMS stands for liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.) The new tests tended to overestimate vitamin D deficiency. According to the LCMS measurements, 33 of the 163 specimens showed vitamin D deficiency. But the Abbott test showed that 45 specimens had vitamin D deficiency and the Siemens test showed that 71 subjects had vitamin D deficiency. Such inaccuracies could lead to overtreatment of vitamin D deficiency, Holmes said.
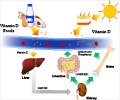
Holmes said inaccurate test results could lead to misdiagnoses of patients and confound efforts of physicians, nutritionists and researchers to identify the optimal levels of vitamin D for good health.People get vitamin D from their diet, from exposure to the sun and from supplements. Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium, which is needed for strong bones. Vitamin D helps increase bone density and decrease fractures. Recent studies have found vitamin D also may decrease the risk of osteoporosis, high blood pressure, cancer, heart disease and diabetes.Populations that may be at high risk for vitamin D deficiency include the elderly, people who are obese, babies who are exclusively breast fed and people who don't get enough sun.
Source-Eurekalert