About
Uterine cancer or endometrial cancer is cancer of the womb and its most common symptom is vaginal bleeding. Treatment and prognosis of uterine cancer depends on the stage of the disease and also the health status of the patient.
Other Nomenclatures - Cancer of Uterus, Endometrial Cancer, Cancer of the Endometrium, Cancer Womb
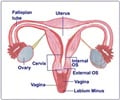
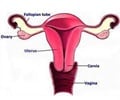
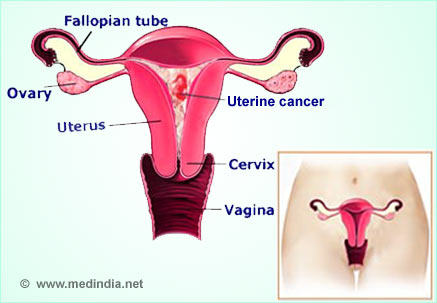
Uterine Cancer or Cancer of Uterus refers to the cancers affecting the uterus or the womb - a pear-shaped female reproductive organ, cradled in the pelvic region between the urinary bladder and the rectum. The uterus is hollow and allows the growth of the fetus during pregnancy.
Anatomy Utetrus - The narrow entrance to the uterus is known as the cervix while the dome – shaped, upper part is the fundus. From this upper region, the fallopian tubes arise and connect to the ovaries, one on each side.
The uterine wall has two layers of tissue. The outer layer of muscular tissue is known as the myometrium while the inner lining, called the endometrium, undergoes a thickening process each month as a part of its preparation for pregnancy. If a woman fails to fall pregnant, the endometrium sheds away its lining and she begins to bleed (or menstruate).
Benign growths within the uterus are most often fibroids. They commonly occur in peri-menopausal women, in their forties. Fibroids usually go away on their own but if they produce symptoms like vaginal discharge, or heavy bleeding, they can be removed laparoscopically. Endometriosis is another benign disease affecting the uterus.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a pre- cancerous state in which the cells of the uterine lining multiply in number ( ‘hyper’- increased, ‘plasia’ –pertaining to cells). This state is most common among women in their forties and is characterized by heavy bleeding, either during menstruation, between periods or after menopause. Hyperplasia predisposes the uterus to develop cancer. The risks can be reduced by hormone treatment or by surgically removing the uterus (called hysterectomy), which is then followed up by regular monitoring and follow up tests and scans.
Uterine tumors normally is seen more commonly in older women and can be malignant or benign. Malignant tumors are life- threatening cancers characterized by uncontrolled cell division. If such a tumor breaks from the uterus and finds its way to the blood stream, or the lymphatic system, then the cancer would spread to other organs such as the liver, lungs and bones. This distribution or spread of cancer is known as metastasis –in this case, it is metastatic uterine cancer. All such cancers that spread in this fashion are life- threatening condition.
There are different types of uterine cancers depending upon the region that is affected. The most common type of uterine cancer is ‘cancer of the endometrium’ which is why uterine cancers are also referred to as endometrial cancer by some.
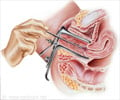
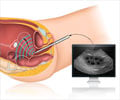
A combination of methods including physical examination, PAP smear, ultra sonography and biopsy of uterine tissue helps in establishing the diagnosis of uterine cancer or to confirm it.
Treatment and prognosis of Uterine cancer depends on the age and the health status of the patient and also on the stage of the cancer and the rate at which the disease progresses in the patient.
Most patients ignore vaginal bleeding and this often can result in late presentation and poor prognosis.
Creating awareness about any abnormal vaginal bleeding especially in the elderly population is the key to early diagnosis and treatment.