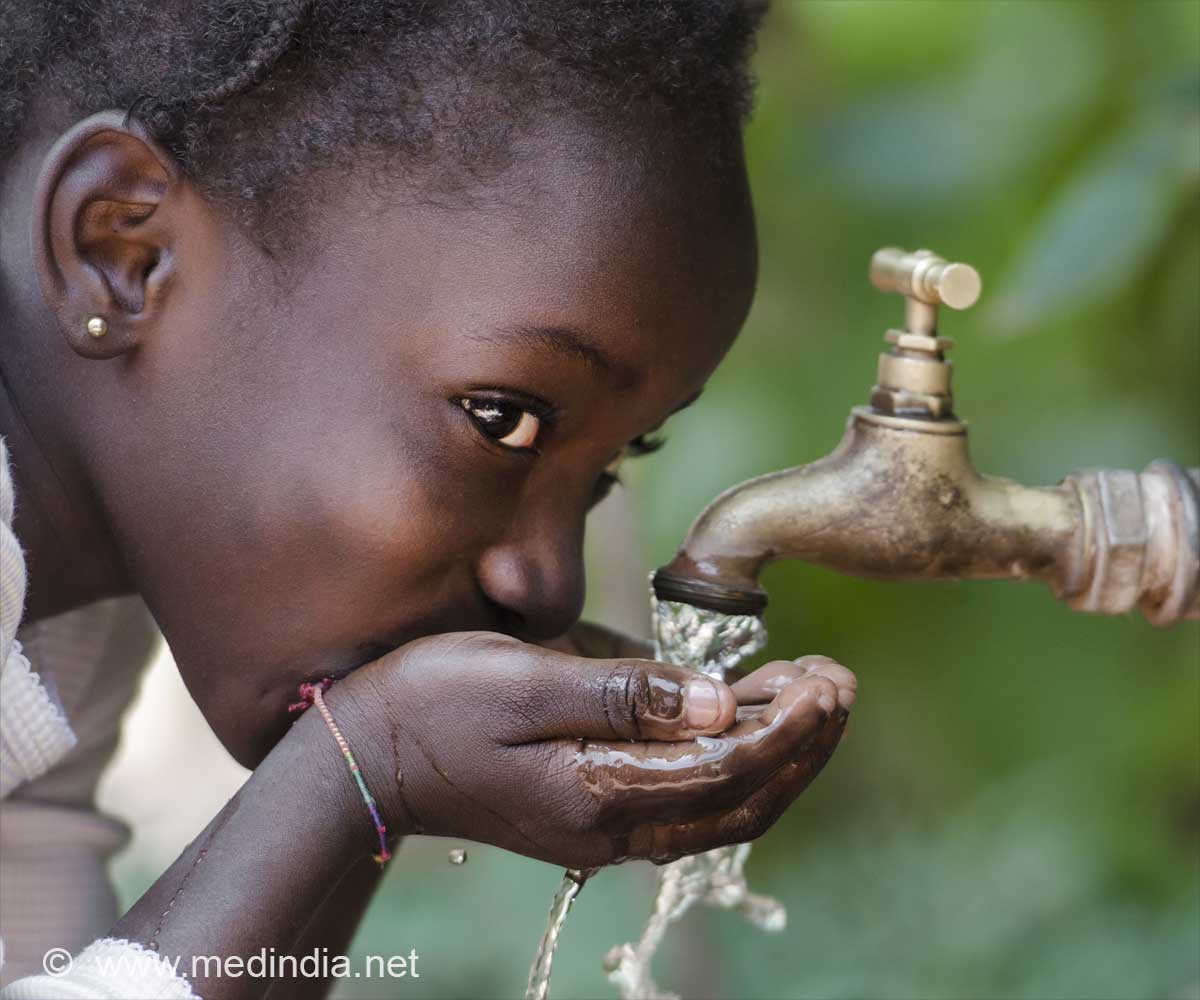
‘Heavy metal water contamination has become a global health issue. However, a new study suggests that a smartphone test can now help millions of people avoid drinking contaminated arsenic water.’
Tweet it Now
The device, developed at the University of Edinburgh, generates easy-to-interpret patterns, similar to volume-bars, which display the level of contamination.A team of researchers believes there is an urgent need to provide simple, affordable, on-site solutions for contaminated water sources.
In resource-limited countries, there is a lack of sufficiently skilled personnel and healthcare facilities to test water for contamination.
The research team say new devices could replace existing tests, which are difficult to use, need specialist laboratory equipment and can produce toxic chemicals.
The contamination of water by heavy metals is a worldwide health issue. UNICEF reports that arsenic-contaminated drinking water is consumed by more than 140 million people worldwide.
Advertisement
An estimated 20 million people in Bangladesh - mostly rural poor - drink contaminated water.
Advertisement
Researchers developed the biosensor by manipulating the genetic code of the bacteria Escherichia coli. They added genetic components to act as amplifiers when arsenic is detected.
Water samples were fed into a plastic device containing bacteria suspended in a gel. This produced fluorescent proteins that were visible in the presence of arsenic.
The research team believes that the approach could be used to detect other environmental toxins, diagnose diseases and locate landmines.
Source-Eurekalert