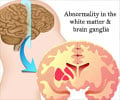
A language model designed to analyze seizure behavior descriptions shows promise in assisting neurologists to accurately identify seizure-triggering brain regions.
- AI helps interpret seizure symptoms to pinpoint seizure-triggering brain zones
- Epileptogenic zones identified accurately in common brain regions with support of language models
- Customized language model created to assist in epilepsy surgical planning
Clinical Value of ChatGPT for Epilepsy Presurgical Decision-Making: Systematic Evaluation of Seizure Semiology Interpretation
Go to source).
Medications help many manage their seizures, but nearly one-third of cases remain resistant to drug treatment. For those patients, surgically removing the brain region responsible for seizures—known as the epileptogenic zone—can be a potential solution, offering periods of seizure freedom.
Despite the promise of surgical intervention, only about 50 to 60% of these procedures successfully eliminate or significantly reduce seizures. One key reason for this moderate success rate is the difficulty in precisely identifying the correct brain area to target. Doctors rely on brain imaging, electroencephalography, and intracranial monitoring to locate the seizure source. They also analyze seizure behaviors and symptoms, a process known as seizure semiology, which plays a crucial role in this decision-making.
TOP INSIGHT
Did You Know?
Over 30% of epilepsy cases do not respond to medication, but AI models can now help decode seizure behavior to improve brain surgery outcomes. #medindia #epilepsy #seizure #AI
Language Differences in Seizure Descriptions
The way seizure behaviors are described can vary widely between epilepsy centers. For instance, two clinicians might use different terms—such as "asymmetric posturing" and "asymmetric tonic activity"—to describe the same movement pattern. This variation creates inconsistencies, which can lead to misinterpretation and complicate surgical planning.Feng Liu, an assistant professor at Stevens Institute of Technology, explains that this inconsistency in medical language poses a challenge for neurosurgeons. Given that seizure semiology is highly descriptive, large language models trained on extensive textual data, such as ChatGPT, may offer a solution by helping to interpret and standardize this information.
Artificial Intelligence Helps Localize Seizure Zones
Liu’s team explored whether ChatGPT could assist in predicting the location of seizure-triggering regions in the brain using descriptions of seizure symptoms. They created an online questionnaire with 100 cases for five board-certified neurologists to complete. The same task was then given to ChatGPT, and its responses were compared to those of the human experts.ChatGPT performed on par with or better than the neurologists in identifying epileptogenic zones in commonly affected areas like the frontal and temporal lobes. However, the neurologists maintained a slight edge in less typical regions such as the insula and the cingulate cortex. These results were recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
Custom Language Model for Seizure Analysis
To build upon this success, Liu’s team developed a specialized large language model specifically for interpreting seizure semiology, naming it EpiSemoLLM. This tailored model runs on a high-powered graphics processing unit server at Stevens Institute of Technology.This new platform is intended to assist neurosurgeons and neurologists during the preoperative phase, helping them make better-informed decisions when planning surgical treatments. According to Liu, the combination of human expertise and artificial intelligence holds the greatest potential for improving surgical outcomes.
By translating the complex language of seizure behavior into more actionable insights, artificial intelligence models like ChatGPT and EpiSemoLLM offer a promising tool in the fight against epilepsy. While they are not a replacement for expert clinicians, their ability to standardize and interpret medical language could enhance the accuracy of epilepsy surgeries and improve quality of life for many patients.
Reference:
- Clinical Value of ChatGPT for Epilepsy Presurgical Decision-Making: Systematic Evaluation of Seizure Semiology Interpretation - (https://www.jmir.org/2025/1/e69173)
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email