Autism spectrum disorder describes lifelong developmental disabilities including difficulty or inability to communicate with others and interact socially.
Highlights
- Pregnant women with low Vitamin D levels are at an increased likelihood of having a child with autistic traits.
- Supplementing Vitamin D to the mother during the first trimester of pregnancy might reduce the chances of autism.
- The active hormonal form of vitamin D cannot be given to pregnant women because it may affect the skeleton of the developing fetus and further research is needed.
TOP INSIGHT
Early dietary supplementation of Vitamin D may help prevent neuro developmental disorders. Vitamin D was crucial for maintaining healthy bones, but the active hormonal form of vitamin D cannot be given to pregnant women because it may affect the skeleton of the developing fetus.
"We found that pregnant females treated with active vitamin D in the equivalent of the first trimester of pregnancy produced offspring that did not develop these deficits."
Low levels of Vitamin D & Autism
In human studies, QBI researchers recently found a link between pregnant women with low Vitamin D levels and the increased likelihood of having a child with autistic traits.
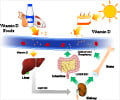
Autism -- or autism spectrum disorder -- describes lifelong developmental disabilities including difficulty or inability to communicate with others and interact socially. Sun exposure is the major source of vitamin D -- which skin cells manufacture in response to UV rays -- but it is also found in some foods.
"Recent funding will now allow us to determine how much cholecalciferol - the supplement form that is safe for pregnant women -- is needed to achieve the same levels of active hormonal vitamin D in the bloodstream," said Dr Luan.
vitamin D interferes with pro-inflammatory transcription factors and signaling pathways, regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory enzymes, and modulates cytokine gene expression, protein production, and signaling.
Reference
- Stephanie Vuillermot et al., Vitamin D treatment during pregnancy prevents autism-related phenotypes in a mouse model of maternal immune, Molecular Autism (2017) http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13229-017-0125-0.
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email