Bariatric surgery may be an effective treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), suggests a new study.

TOP INSIGHT
Gastric bypass could be the best surgical option for NAFLD patients in whom excess fat is stored in the liver.
Read More..
NAFLD is more common in people who have certain conditions, including obesity and conditions that may be related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes. Researchers have found NAFLD in 40% to 80% of people who have type 2 diabetes and in 30% to 90% of people who are obese.
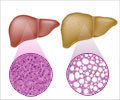
When the fat builds up in the liver and causes inflammation and damage, it is known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to scarring of the liver--a potentially life-threatening condition called cirrhosis.
"NAFLD is strongly associated with obesity, and the prevalence of both diseases is notably increasing," Borges-Canha said. "There is a concerning lack of effective treatment options for patients with NAFLD." No medicines have been approved to treat NAFLD. The current recommended treatment is weight loss, which can reduce fat in the liver, inflammation, and fibrosis, or scarring.
The new study evaluated the effects of bariatric surgery on liver function and indicators of liver inflammation and scarring. The researchers included 1,995 morbidly obese patients who underwent bariatric surgery between January 2010 and July 2018.
FLI is an algorithm that predicts liver steatosis or fat deposition. It is based on waist circumference, body mass index and levels of triglyceride and an enzyme found in the liver called γ-glutamyltransferase.
Gastric sleeve was associated with a greater reduction of liver enzymes and both FLI and BARD compared with gastric band. However, gastric sleeve led to a smaller reduction of FLI and BARD compared with gastric bypass surgery.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email