Initiating stroke treatment just 15 minutes faster can save lives and prevent disability, finds new study.
TOP INSIGHT
Reducing the time interval between hospital admission and treatment could potentially save more lives and improve patients’ quality of lives after the procedure.
The researchers looked at stroke patients' treatment results in light of their "door-to-puncture" time -- that is, the interval from their arrival at the hospital to the time their treatment began.
The data showed that for every 1,000 people whose door-to-puncture time was 15 minutes sooner, 15 fewer died or were discharged to hospice care, 17 more were able to walk out of the hospital without assistance and 22 more could care for themselves after being discharged from the hospital. Researchers found that patients' median time from arriving at the hospital to the beginning of treatment was one hour, 27 minutes, and the median time from the onset of symptoms to treatment was three hours, 50 minutes.
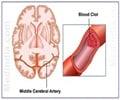
All of the patients in the study were treated with endovascular reperfusion therapy, which is used to treat strokes caused by a blockage in one of the major arteries of the brain.
The study is one of the largest to quantify the number of patients per thousand that could be saved by earlier stroke treatment, and to do so using real-world data as opposed to a clinical trial, according to Dr. Reza Jahan, the study's co-lead author and a professor of interventional neuroradiology at the Geffen School of Medicine.
Based on the study's results, saving 15 minutes off of treatment time could potentially improve results for thousands of people each year.
"We're trying to improve treatment with better staffing on off hours and getting doctors to the hospital quicker when they're on call," Jahan said. "Patients who arrive at the hospital at 2 a.m. should be treated no differently than people who arrive at 2 p.m."
Treatment delays also are more likely for people who live alone or fail to recognize their own stroke symptoms.
Based on the study results, the American Heart Association has already published new goals regarding how fast patients should be treated at comprehensive stroke centers, Jahan said.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email