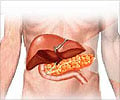
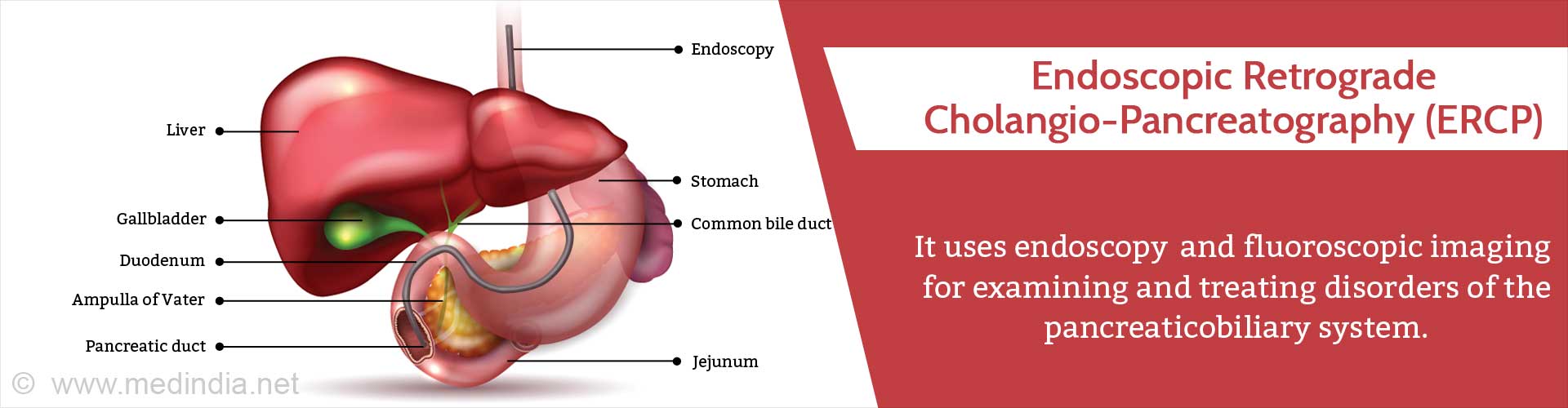
Glossary
Cholangitis: An infection of the bile duct, which is usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum.Jaundice: This is the visible sign of an underlying disease process usually involving the liver, where there is elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood, which imparts a yellow color to the skin, white of the eyes and mucus membranes, darkening of the urine and light colored stool.
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): A special type of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique that produces detailed images of the hepatobiliary and pancreatic systems, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, pancreatic and bile ducts.
Malignancy: The state or presence of a malignant tumor; cancer.
Sphincter of Oddi Manometry (SOM): It is a procedure in which a catheter is passed into the bile and/or pancreatic duct during ERCP to measure the pressure of the biliary and/or pancreatic sphincter. It is considered the gold standard diagnostic modality for sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD).
Stent: A stent is a tubular device made of plastic or metal that is primarily used to establish patency (degree of openness) of a blocked bile or pancreatic duct.
Stricture: An abnormal narrowing of a body passage, especially a tube or a canal due to the formation of fibrous tissue. The term refers to both the process of narrowing and the narrowed part itself.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email