Patients undergoing ERCP have a risk of developing post-ERCP pancreas inflammation. Rectal Indomethacin is effective in protecting post-ERCP pancreatitis.
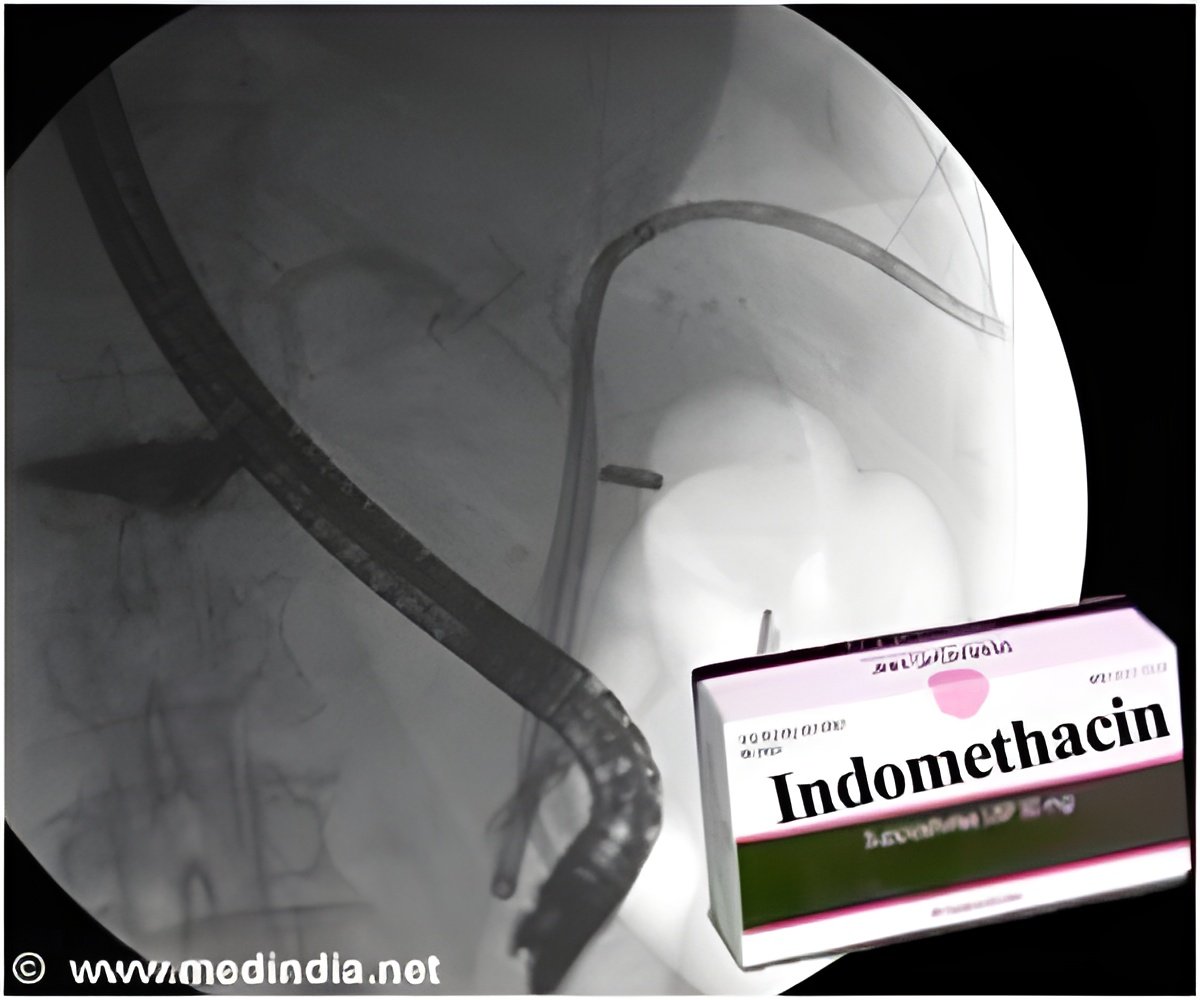
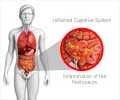
Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas. The chief complaints in post-ERCP pancreatitis are upper abdominal pain and raised level of pancreatic enzymes. Post-ERCP pancreatitis is a complication resulting in one quarter of patients undergoing ERCP. Although the condition has been researched for years, this study is the first breakthrough revealing how post-ERCP pancreatitis can be effectively prevented.
A randomized placebo-controlled trial was conducted where 602 patients were given rectal indomethacin or placebo soon after ERCP. They were given two Indomethacin 50-mg rectal suppository and matching placebo immediately after the ERCP.
B.Joseph Elmunzer, M.D. gastroenterologist and the lead author of the study stated, "ERCP is a very important procedure that can provide life-saving interventions for people who need it, although it is considered the most invasive of all the endoscopic procedures and it does have risks associated with it."
The pancreas suddenly becomes swollen in post-ERCP pancreatitis. According to the experts, this complication results in approximately $150 million being spent on health care services per annum.
It was found that the patients who received indomcethacin-the anti-inflammatory drug rectally soon after the ERCP procedure had less chances to be hospitalized with pancreatitis. Incidentally, the cost of a single dose of indomethacin is $5.
About 16.9 percent of placebo administered patients developed pancreatitis.
Evan L.Fogel, the gastroenterologist and co-author of the study mentioned, "Our findings showed that one dose of indomethacin given immediately after ERCP significantly reduced the incidence of post-ERCP pancreatitis in patients at elevated risk for this complication”.
“We found that prophylactic indomethacin decreased the severity of post-ERCP pancreatitis and was associated with shorter hospital stays", they said.
Joseph Elmunzer et al said that their study findings provided simple treatment for preventing post-ERCP pancreatitis. Elmunzer finally concluded that the results obtained with rectal administration of indomethacin were protective against post-ERCP pancreatitis.
The experts are of the opinion that the results of the trial have already affected the clinical practices.
References:
A Randomized Trial of Rectal Indomethacin to Prevent Post-ERCP Pancreatitis; Joseph Elmunzer et al; N Engl J Med 2012; 366:1414-1422
Source-Medindia
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email