- Vinegar: Medicinal Uses and Antiglycemic Effect - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1785201/)
- Ostman E, Granfeldt Y, Persson L, Björck I. Vinegar supplementation lowers glucose and insulin responses and increases satiety after a bread meal in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005 Sep;59(9):983-8. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16015276)
- Shishehbor F, Mansoori A, Sarkaki AR, Jalali MT, Latifi SM. Apple cider vinegar attenuates lipid profile in normal and diabetic rats. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008 Dec 1;11(23):2634-8. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19630216)
- Kondo T, Kishi M, Fushimi T, Kaga T. Acetic acid upregulates the expression of genes for fatty acid oxidation enzymes in liver to suppress body fat accumulation. J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jul 8;57(13):5982-6. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19469536)
- Kondo S, Tayama K, Tsukamoto Y, Ikeda K, Yamori Y. Antihypertensive effects of acetic acid and vinegar on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2001 Dec;65(12):2690-4. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11826965)
- Liatis S, Grammatikou S, Poulia KA, Perrea D, Makrilakis K, Diakoumopoulou E, Katsilambros N. Vinegar reduces postprandial hyperglycaemia in patients with type II diabetes when added to a high, but not to a low, glycaemic index meal. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010 Jul;64(7):727-32. Epub 2010 May 26. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20502468)
- Johnston CS, Steplewska I, Long CA, Harris LN, Ryals RH. Examination of the antiglycemic properties of vinegar in healthy adults. Ann Nutr Metab. 2010;56(1):74-9. - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20068289)
About
Vinegar comes from the French word meaning ‘sour wine’ and is made from a fermentable carbohydrate source. When the source is apple juice, it is known as apple cider vinegar. Why is it called cider vinegar? That’s because it is made from the fruits.
When the vinegar is made from distilled alcohol obtained from the grains or the starch of cereals or potatoes, it is called white or distilled vinegar. The distilled vinegar has an acidity of 4 percent, while the acidity of cider vinegar ranges from 5 to 6 percent.

The acetic acid in apple cider vinegar (ACV) is what gives it its tanginess and tart flavor. However, diluted acetic acid and vinegar is not the same thing.
According to the FDA, ‘Diluted acetic acid is not vinegar and should not be added to food products customarily expected to contain vinegar’. Basically, apple cider vinegar or ACV contains vitamins (B1, B2, B6, and C), minerals (magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus and calcium and iron in small amounts), nonvolatile organic acids such as tartaric acid, citric acid, malic acid and lactic acids, and polyphenolic compounds like gallic acid, catechin, caffeic acid and ferulic acid.
Medicinal Use of Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) has been used since ages in traditional remedies as a miracle healer for migraine headaches, hypertension, diabetes, chronic fatigue, external wounds, and even to kill head lice and fight inflammation. It is also used as a weight loss agent. So much so, people are trying out the Apple Cider Vinegar Diet to shed pounds. But, are these claims true? Are there scientific evidences proving the effectiveness of ACV to treat these conditions? Here’s a rundown on some of these claims.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email
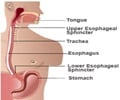








How much vinegar and water should be used to lower blood sugar? Thanks!