- Five Tips For Eye Health - (http://www.eatingwell.com/nutrition_health/healthy_aging/five_tips_for_eye_health)
- How to Keep Your Eyes Healthy - (http://www.webmd.com/eye-health/good-eyesight)
About
Eye problems may present as blurry vision or simply a minor headache, but they can affect your life in more ways than one. While most vision problems are genetic, there are some that can arise as a result of lifestyle habits, physical injury and even ageing. Read on to discover more about some common eye problems, their symptoms, diagnosis and correction.
Refractive Errors -
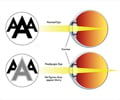
Hypermetropia: Also known as farsightedness, hypermetropia is a condition wherein the individual is able to clearly view objects at a distance, but is however, unable to view objects that are nearer. This is because the rays of light from the object do not fall exactly on the retina, but much behind it. Family history is of utmost importance in this condition.
Headache, blurred vision and difficulty in reading words that are near are some common symptoms of hypermetropia. Diagnosis of this condition is done by Cyclo refraction test wherein eye drops are administered to relax the ciliary muscles of the eye, so that the exact degree of hypermetropia can be found.
Treatment of this condition may be done by a LASIK eye surgery in which the cornea of the eye is re-shaped to make it steeper. One can also use contact lenses or spectacles. However, it should be noted that the contact lenses must be light weight and anti-reflective, since the eye tends to look enlarged if a heavy contact lens is worn.
Myopia: This condition is the exact opposite of hypermetropia - the individual is able to view nearby objects clearly, but the objects placed far away appear blurred. In such an individual, the eyeball is longer than in a normal individual, causing the light from a faraway object to fall in front of the retina.
Characterized by headaches and eye strain, myopia is common among school children. Contrary to popular belief, reading in dim light and watching too much TV is NOT responsible for causing myopia. Regular annual examinations should be done for school-going children to detect the presence of myopia. The child will simply be asked to read off the Snellen chart placed 20 feet away by using lenses of different strengths. Eye drops may also be administered to relax the ciliary muscles and give an accurate correction.
LASIK and Epi-LASIK are suggested for individuals over 18 years of age, having stable power for over 6 months and not suffering from any severe ophthalmic condition such as glaucoma and cataract. Contact lenses can be used to enhance cosmetic appearance; however, it is suggested that children use spectacles until they reach maturity.
Astigmatism: Often combined with near-sightedness or far-sightedness, astigmatism is a condition where the corneal shape of the eye is affected, leading to blurred vision.
Headache, accompanied by pain in the eyes and blurred vision are common symptoms of low-degree astigmatism. Corneal topography-a technique that makes three-dimensional maps of the cornea, is done to rule out the possibility of diseases like keratoconus. Toric contact lenses, spectacles with spherical and/ or cylindrical lenses are recommended. For patients who have passed the corneal topography successfully, LASIK eye surgery can be considered.
Age-related Disorders -
Presbyopia: Ageing eyes or presbyopia refers to the onset of visual impairment as a person crosses 40 years of age. This usually happens because the ciliary muscles of the eye become weak with age, and the eye loses its ability to focus at different distances.
Characterized by eye strain, blurry vision and headaches, presbyopia hampers some precision requiring day-to-day activities such as threading a needle, and so on. This ocular condition is diagnosed by a simple near vision chart and can be corrected either by LASIK surgery, or by use of multi-focal lenses.
Cataract: The human eye is made up of protein and water. As the individual ages, the proteins in the eye tend to cluster together, clouding a part of the eye, and making it look foggy in appearance. This is known as cataract.
Being painless, cataract is often characterized by simple, easy-to-note symptoms such as reduced sharpness and brightness of objects, inability to view objects clearly even after using glasses, and decreased vision in bright lights. It can be easily detected by a 5-minute test known as the slit-lamp examination. Treatment for cataract is a surgery that replaces the clouded lens with an artificial lens made up of silicone or polymer acrylate. Left untreated, cataract can lead to blindness.
Age-related macular degeneration: Age-related macular degeneration, as the name suggests, occurs in the elderly, and affects the macula of the eye (central portion of the retina). It may present itself as either a gradual breakdown of the macula, or by formation of abnormal blood vessels in the macula.
Age-related macular degeneration is most commonly noted by 2 symptoms-blurry vision and black spots. It is diagnosed by using an ophthalmoscope and an Amsler grid. Though there is no cure at present for this condition, researchers say that including more green vegetables in your diet and improving lifestyle habits can make a huge difference in shunning away many other age-related ocular manifestations.

Other Eye Problems -
Dry eyes: A very common eye concern, especially among people living in urban areas, dry eyes may show symptoms like redness, painful itching, burning sensation and whitish discharge. Most common causes of dry eye are exposure to pollutants, heat, dust, wind etc. Sitting near an air conditioner for too long can also cause eye problems. Avoid staying in the sunlight for too long without sunglasses.
Conjunctivitis: Commonly observed during warm and humid seasons, conjunctivitis is basically an infection of the membrane lining the surface of the eyes and eyelids, leading to redness, swelling, inflammation, excessive tear production and crusting. Both viral and bacterial
Lazy eye: An early childhood condition wherein the eyesight in one eye of the child does not develop as it should, lazy eye can leave the child visually impaired in that eye for life if not treated at an early stage. This condition starts appearing in early childhood and can make the brain biased, forcing it to focus on one eye only, virtually ignoring the lazy eye. If the ‘lazy’ eye is not stimulated within the early stages, it can hamper the maturation of the visual brain cells, leaving the child visually impaired. The best treatment is to patch the better eye so that the child is forced to focus on the ‘lazy’ eye and develop his vision in the affected eye at the right time.
Stye: A stye is basically a minor inflammation of the oil gland just at the edge of the eyelid which can hurt when you blink. Styes can be easily prevented by removing make-up before going to bed and by avoiding the use of dirty hands to rub the eyes.

Diabetic retinopathy: Diabetic blindness or diabetic retinopathy is one of the severe complications of diabetes which involves swollen, leaky blood vessels rupturing in the retina and blocking the vision of the individual. Controlling blood sugar and getting regular eye check-ups done is very important for all diabetic patients.
Uveitis: This painful condition occurs as a result of inflammation of the uvea of the eye, possibly due to different underlying causes like family history, auto-immune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, and infections like TB and toxoplasmosis. This condition is characterized by a severe pain and swelling in the eye, often radiating to the head. Sensitivity to sunlight and inflammation of the eye is also seen. Ophthalmologists usually prescribe steroids to tackle this condition.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email