- Tibial plateau fracture - (http://radiopaedia.org/articles/tibial-plateau-fracture)
What is a Tibial Plateau / Bumper Fracture?
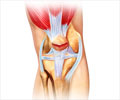
A tibial plateau/bumper fracture occurs at the top of the shin bone and involves the cartilage area of the knee joint. Fractures of the tibial plateau affect knee motion, stability, and alignment.
A tibial plateau/bumper fracture is generally considered serious because of the critical role in weight-bearing. When this kind of fracture occurs in and around the joint, the joint is at risk of developing injury-related arthritis. Early diagnosis and clinical intervention are necessary to prevent post-traumatic arthritis.
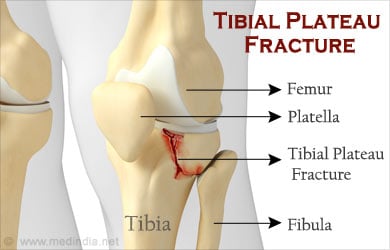
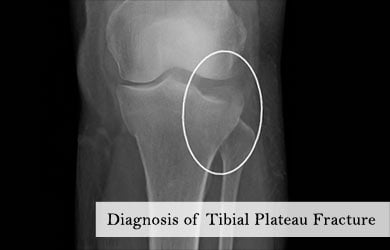
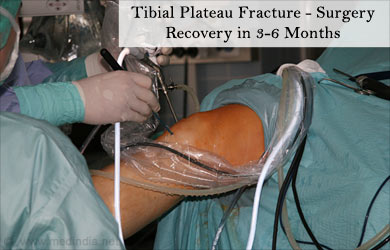
A tibial plateau/bumper fracture is generally diagnosed both clinically and through imaging techniques. X-ray and MRI scans are the usual diagnostic tests. Treatment depends on the nature of the fracture (non-displaced/displaced). A displaced fracture usually requires surgery to realign the displaced bones and restore alignment and stability to the knee joint. Recovery from a tibial fracture usually varies between 3 to 6 months depending on the age and the health of the patient.
How Does a Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fracture occur?
Elderly people above 50 years of age are at risk of this type of fracture. In menopausal women, this type of fracture is most commonly attributed to osteoporosis.
Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fractures are of Two Types:
- Low energy – fractures occur in osteoporotic bones and are typically depressed fractures.
- High energy – fractures occur due to external trauma, like injuries.
Risks of a Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fracture
When this kind of fracture occurs in and around the joint, the joint is at risk of developing injury-related arthritis. It is not uncommon to observe injuries to the ligaments like the anterior cruciate ligament (one of the four major ligaments of the knee), collateral ligaments (also known as medial collateral ligament or tibial collateral ligament is another major ligament in the knee. It is on the inner (medial) side of the knee joint), menisci (a meniscus is a piece of cartilage found in the joint space where two bones meet. Menisci protect and cushion the joint), and articular cartilage (tissue covering the end of the bones) A tibial plateau/bumper fracture is generally considered serious because of the critical role in weight-bearing.
Early diagnosis and clinical intervention are necessary to prevent posttraumatic arthritis.
Symptoms of a Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fracture
Low energy fractures often present with mild pain and slight difficulty in walking. To avoid a misdiagnosis it is important to confirm/rule out a tibial plateau/bumper fracture through an x-ray or CT scan.
Diagnosis/Testing of a Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fracture
The most common imaging techniques used are:
- X-ray
- CT scan – useful in assessing the extent of bone damage
- MRI scan – useful in assessing the extent of soft tissue damage
Clinical examination is important to check for loss of toe/ankle movement or loss of sensation. This is critical to rule out injury to blood vessels and nerves.
Treatment for a Tibial Plateau/Bumper Fracture
A non-displaced fracture does not usually require surgery and heals with total rest (about 3 months). A displaced fracture usually requires surgery to realign the displaced bones and restore the alignment and stability to the knee joint.
Non-displaced fracture: This type of fracture occurs when the tibia sustains a hairline crack without the separation of bones. The bones remain aligned in their proper position. This type of fracture heals on its own and generally does not require surgical intervention. The fracture requires a total of 3 months rest without any stress and load on the knee joint. The patient must not walk and needs to exercise caution in case the fracture does displace.
Displaced fracture: This type of fracture occurs when the bone breaks into two or more fragments. This type of fracture requires surgical intervention to realign the bones and restore stability to the knee joint.
Surgery involves placement of screws and plates to restore the alignment to the knee joint. Screws and plates are used to hold the bone fragments in place. Screws alone are used when only one piece of bone is broken. A plate is used when the tibial plateau requires extra support. The plate is placed along the bone to help the fragments heal in place.
Recovery and Outcome
Patients must take precautions not to engage in weight bearing including walking on the injured knee before the fracture heals fully. This can result in displacement of the knee requiring surgery. Arthritis can be prevented by ensuring accurate re-alignment of the fracture.
Therapy is aimed at restoring full movement to the knee joint and aiding the bones to heal correctly in position. Early ambulation is recommended to avoid loss of knee movement. As muscles atrophy post the fracture and surgery, movement maybe painful requiring intensive physiotherapy. Physiotherapy and rehabilitation are aimed at getting the patient back to routine normal activities.

 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email