- Sheen AJ, Iqbal Z. Contemporary management of ‘Inguinal disruption’ in the sportsman’s groin. BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation20146:3 DOI - (10.1186/2052-1847-6-39)
What is Inguinal Disruption / Gilmore's Groin?
Gilmore’s groin is also known as sportsman’s groin or athletic pubalgia. It is named Gilmore’s groin after Jerry Gilmore, who first described the condition not too long ago in 1980. The term ‘inguinal disruption’ is currently the most preferred term for the condition.
The groin is the fold where the lower abdomen joins the thigh. Deep inside this region is the pubic bone, which gives attachment to several muscles of the pelvic region, thigh and the abdomen. The bone has a small projection on its inner side, called the pubic tubercle. Attached to it is the inguinal ligament; the inguinal ligament forms the base of the inguinal canal, which is a weak area of the groin, from where hernias can arise.
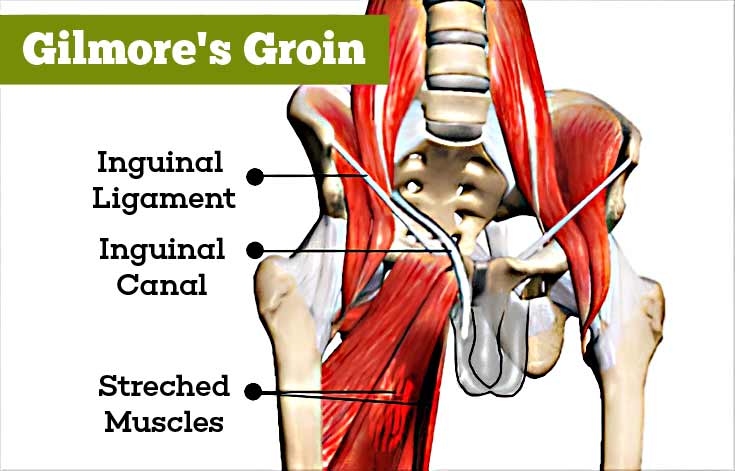
Inguinal disruption results in pain in the groin and may be associated with a tear or injury of a muscle or a ligament, or trapping of a nerve in the region. Though also called sport’s hernia or sportsman’s hernia; a hernia is absent.
What are the Causes of Gilmore's Groin / Inguinal Disruption?
Gilmore’s groin is typically noted in athletes though it may affect non-sportspersons as well. It is caused by sports like rugby or soccer that involve kicking or twisting movements, which cause excessive tension in the groin. It is uncommon for cyclists and swimmers.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Gilmore's Groin / Inguinal Disruption?
Symptoms and signs of inguinal disruption include the following:
- Deep pain in the groin of an athlete which:
- May appear suddenly after exercise or over a long duration. The patient may not always remember the triggering event for the pain
- Aggravates with coughing or sneezing or any twisting movements
- Can spread to the neighboring areas like the inner aspect of the thigh, the perineum or across the midline of the body
- Can be elicited by applying pressure at the pubic tubercle
- Makes it difficult for the patient to take part in sports
- Hernia of the inguinal region is absent
- The patient experiences weakness in the groin while trying resisted sit-ups
- The patient may not find relief from the pain even after multiple visits to orthopedic specialists

How is Inguinal Disruption / Gilmore's Groin Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Gilmore’s groin is made based on:
- History of the patient
- Physical examination of the patient
- Imaging studies like ultrasound and MRI. These tests are mainly useful to rule out other conditions that could be causing the pain.
How to Treat Inguinal Disruption / Gilmore's Groin?
Since inguinal disruption commonly affects athletes, many of whom may be in professional sports, treatment should ensure a complete and early recovery. Treatment of inguinal disruption includes the following:
- Adequate rest to promote healing of the damaged tissue
- Painkillers to reduce the pain
- Steroid injections in some cases to reduce inflammation
- Physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles of the groin
- Physical rehabilitation following surgery to enable the patient to get back to sporting activities
- Surgery, which may be necessary in some cases to release the stress on the groin or to repair any tears or strengthen weak areas. Surgery may be done either through a laparoscope or as an open procedure. Several procedures have been used, depending on the preference of the surgeon

 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA
 Email
Email




