The most common ma-lignant primary brain tumor in adults is glioblastoma.
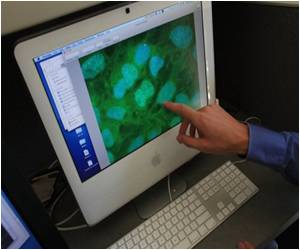
Thus, novel therapeutic strategies must to be investigated for the development of a more effective treatment strategy. Stem cell-based therapies are emerging as novel cell-based delivery vehicle for therapeutic agents.
Prof. Qingjun Zhang and team from the Department of Neurosurgery, Peking University People's Hospital proposed that umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells may have similar targeting capabilities for glioma.
The researchers found that human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells demonstrated excellent glioma-specific targeting capacity in established rat glioma models after intratumoral injection or contralateral ventricular administration in vivo. These findings were published in the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 8, No. 22, 2013).
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email