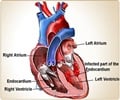
A study suggests that transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) appears to be an effective alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement.
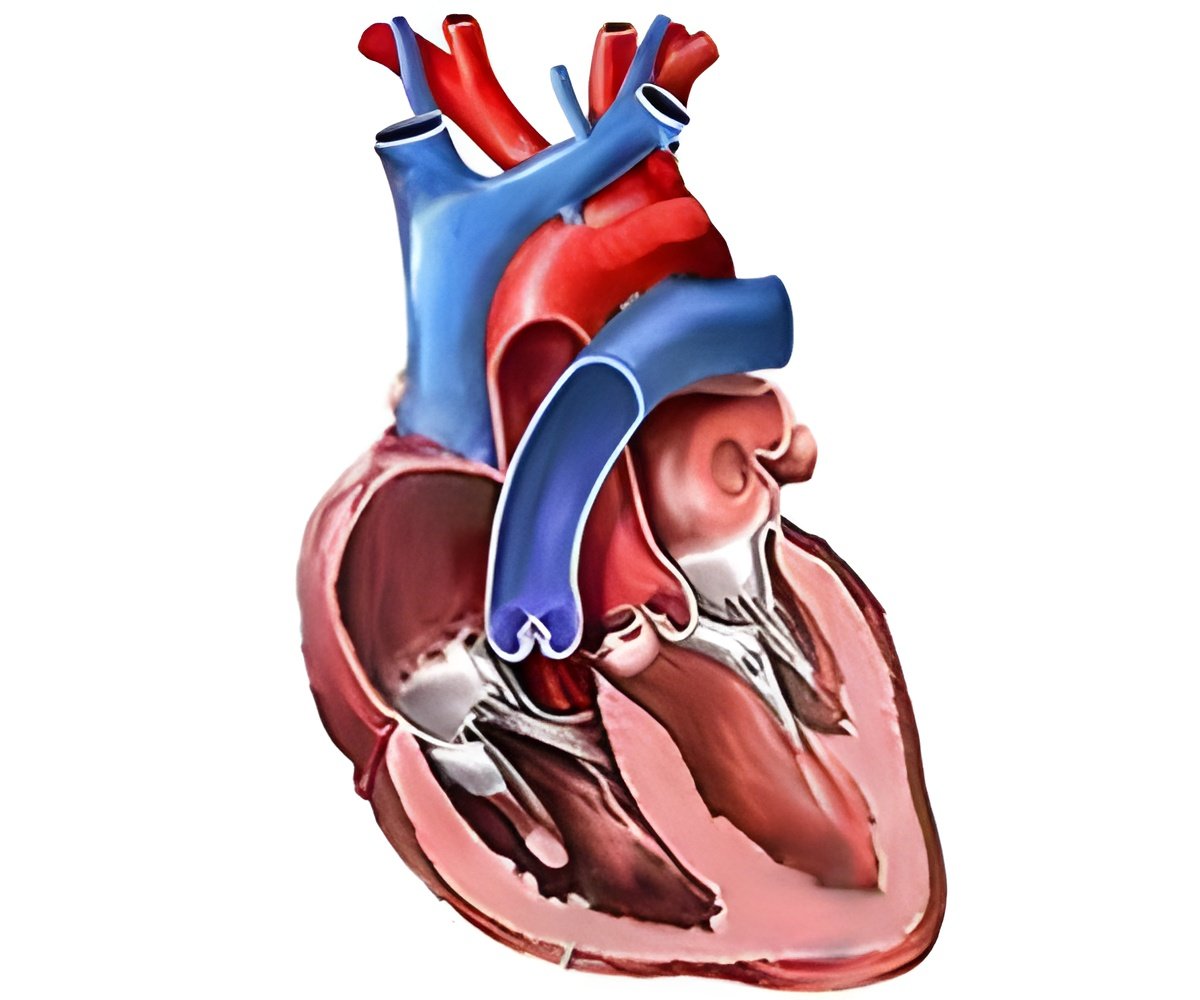
Mansanori Yamamoto, MD, and Emmanuel Teiger, MD, both from the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU)-Henri Mondor in Creteil, France, led a group of researchers examining TAVI results in very elderly patients.
"Our study found TAVI to provide acceptable clinical results in very elderly populations," said Dr. Yamamoto. "Elderly patients generally require more time to recover after invasive treatments, such as AVR, so TAVI may have advantages because earlier mobility plays a significant role in maintaining neuromuscular strength and physical function in elderly patients. Smaller incisions allow faster resumption of physical activity and therefore full recovery."
For the study, researchers collected data from 2,254 patients age 80 years and older who underwent TAVI between January 2010 and October 2011 at any of the 34 hospitals participating in the French national TAVI registry (FRANCE-2 Registry). For the analysis, patients were divided into three categories based on age: 80-84 years (867 patients), 85-89 years (1,064 patients), and ≥90 years (349 patients).
High procedural success was achieved in every patient age group (97.8%, 96.3%, and 97.1%, respectively), and both length of hospital stay and time in the intensive care unit were similar in all groups.
Cumulative mortality rates for the entire patient population were 9.9% at 30-days and 23.8% at 1-year post-surgery. Mortality rates at 1-year were higher among patients in the 85-89 and ≥90 year age groups, compared with the mortality rate in patients in the 80-84 year age group (26.1%, 27.7%, and 19.8%, respectively).
For a copy of the study, contact Cassie Brasseur at 312-202-5865 or [email protected].
The Annals of Thoracic Surgery is the official journal of STS and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association.
Source-Newswise
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email