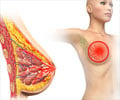
An antibody found in the blood of sharks could help tackle breast cancer, say researchers.

Biologists from the University of Aberdeen have been awarded 345,660 Australian dollars by Scottish cancer research charity the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR) to carry out a three-year study.
Their work will focus on two molecules, HER2 and HER3, found on the surface of cancer cells which, when they pair-up, are responsible for signalling cancer cells to grow and divide.
Potentially, IgNAR antibodies could be used to stop these molecules from working and sending the signal.
Dr Helen Dooley who is from the university's School of Biological Sciences and will lead the study sais that IgNAR antibodies are interesting because they bind to targets, such as viruses or parasites, in a very different way to the antibodies found in humans.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email