Positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy produces meaningful benefits and improves sleep-related quality of life for people with obstructive sleep apnea.

‘Older patients and those in a higher socioeconomic subgroup have better quality of life measures after PAP therapy.’





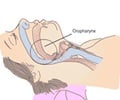
Nearly 30 million adults in the U.S. have obstructive sleep apnea, a chronic disease that involves the repeated collapse of the upper airway during sleep. Common warning signs include snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness. One treatment option for sleep apnea is PAP therapy, which uses mild levels of air pressure, provided through a mask, to keep the throat open while you sleep.The study involved 2,027 patients with sleep apnea who began PAP therapy between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 31, 2014. Participants had a mean age of 56 years, and about 54 percent were men. General quality of life measures, such as mobility and usual activity, was assessed using the European Quality of Life-5D (EQ-5D) questionnaire. Sleep-specific quality of life was examined with the Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire (FOSQ), which assesses the effect of sleep disorders and excessive daytime sleepiness on activities of daily living such as productivity and intimacy. Scores before and after up to one year of PAP therapy were compared.
Results also show that older patients and those in a higher socioeconomic subgroup had better quality of life measures after PAP therapy.
"Our study also serves as a basis for targeted efforts to optimize quality of life in younger adults and lower socioeconomic subgroups," said Walia. "This information will guide clinicians in terms of expected quality of life outcomes with sleep apnea treatment." The American Academy of Sleep Medicine previously identified quality of life as one of three sleep apnea outcome measures that clinicians can track to optimize care for adult patients. Implementation of a quality assurance program to track these quality measures can help improve patient outcomes, reduce the public health burden of sleep apnea, and provide a measurable standard for evaluating and managing sleep apnea.
The study is published in the the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
Advertisement