The more episodes of depression a person has, the greater the reduction in hippocampus size - an area of the brain responsible for memory and emotion.
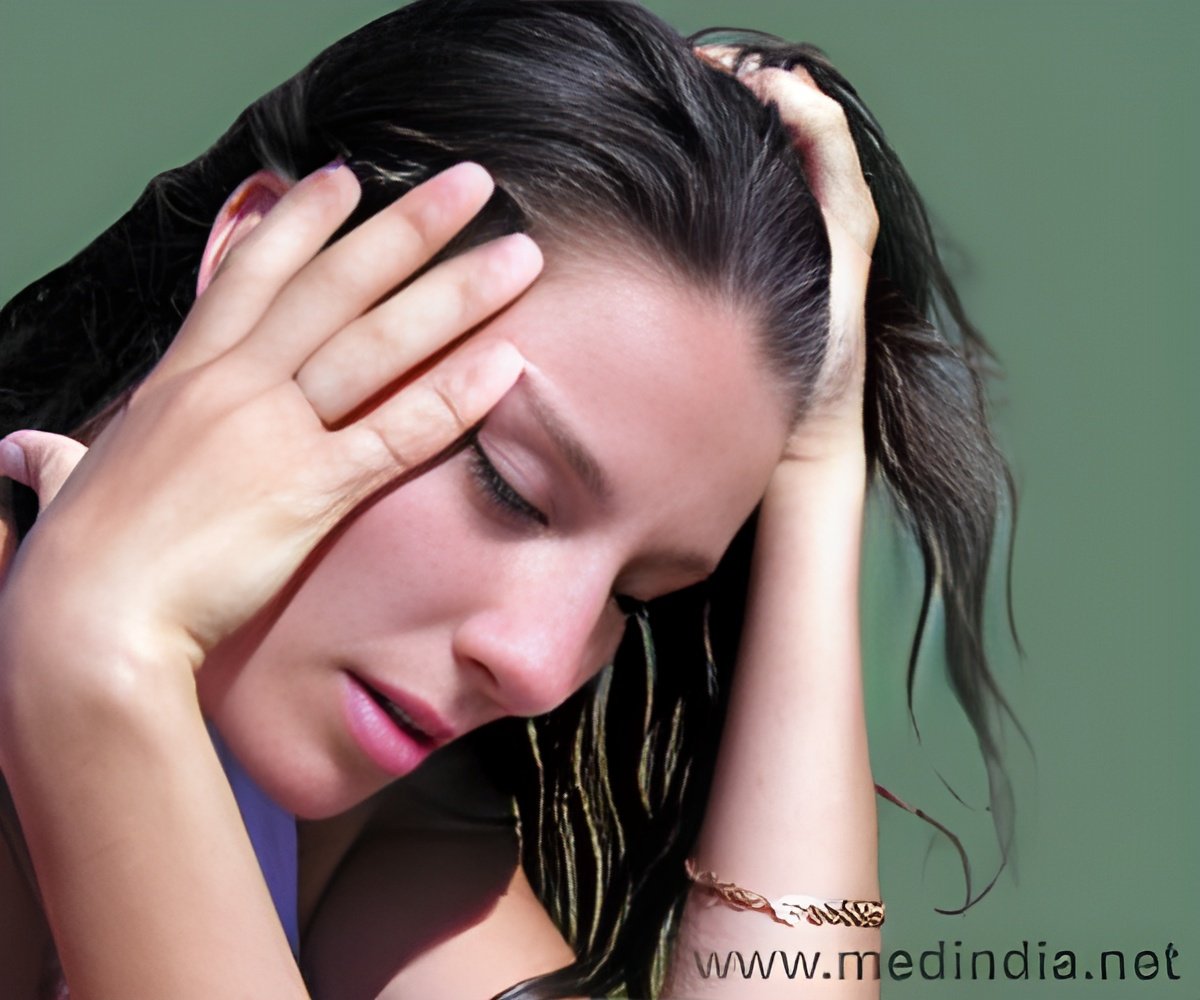

"The more episodes of depression a person had, the greater the reduction in hippocampus size," said Hickie, from University of Sydney’s brain and mind research institute and member of the large study.
The participants experienced their first depressive episode when they had a normal hippocampus size. The shrinking began afterward.
For the study, 15 research institutes from across the world collaborated and examined the data of 8,927 people, 1,728 of whom had major depression and the rest of whom were healthy.
The researchers found that 65% of the depressed participants had recurrent depression and it was these people who had a smaller hippocampus.
"Persistent depression does more harm to the hippocampus the more you leave it untreated. The damage to the brain comes from recurrent illness," Hickie said. "Treating depression effectively does not just mean medicines. Social interventions are just as important," the author said.
Source-IANS
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA




 Email
Email