Novel Acousto Thermal Shift Assay (ATSA) can diagnose diseases of the blood such as sickle cell disease with sensitivity and accuracy and in only one minute, reports a new study.
TOP INSIGHT
Sickle cell disease affects hemoglobin levels, the molecule in red blood cells that delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body.
Proteins have a distinct solubility at a particular temperature. When the protein is mutated or when one bonds to another, the solubility alters. By assessing solubility at various temperatures, experts can find whether the protein has been mutating.
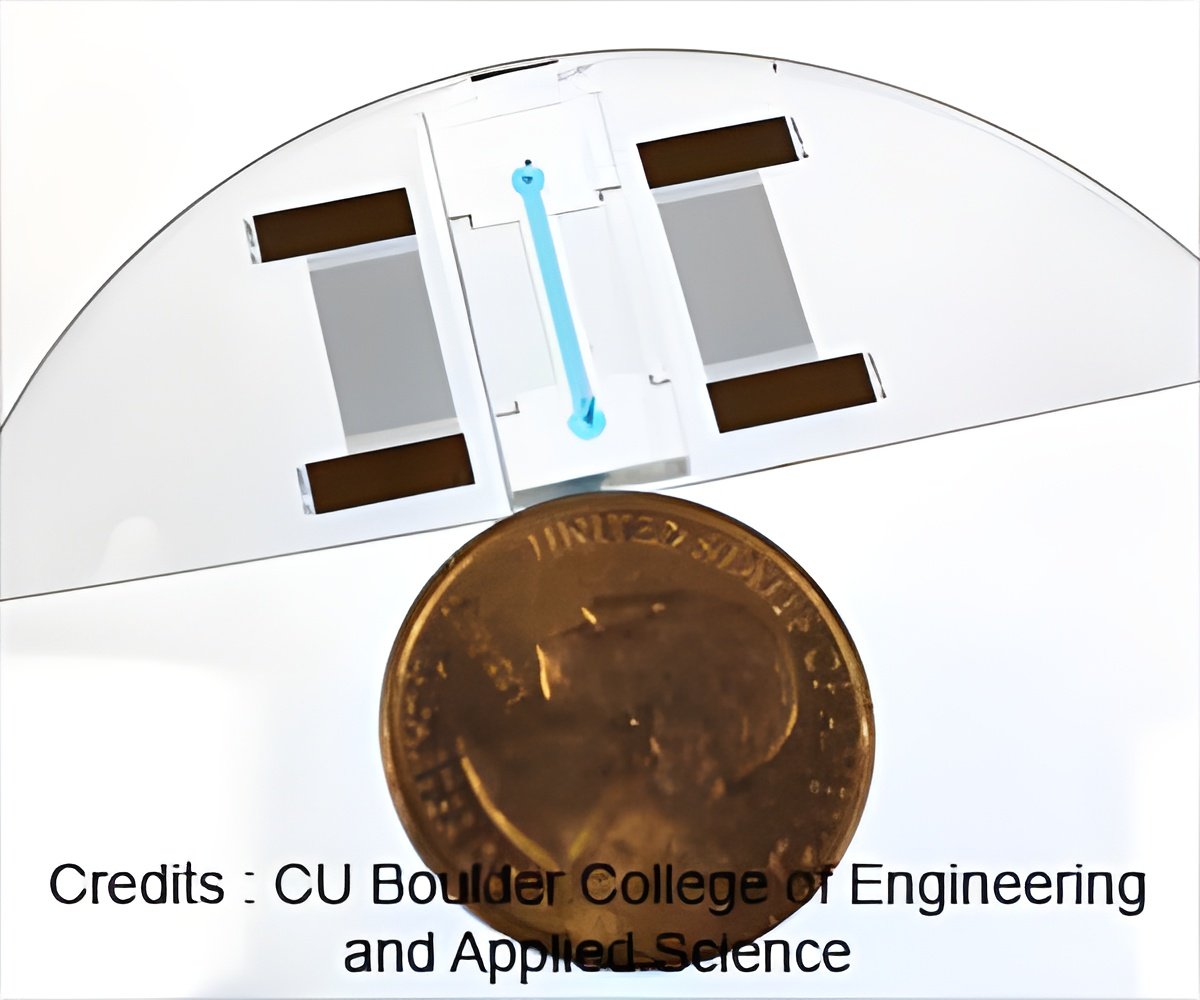
The investigators used Acousto Thermal Shift Assay (ATSA) to assess protein stability under altering conditions. ATSA uses ultrasound, or high-amplitude sound waves, to heat a protein sample. The tool then assessed data continuously, recording how much of the protein has melted at every fraction of change in degrees Celsius.
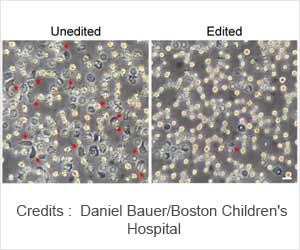
"Our design is seven to 34 times more sensitive," stated Ding. "The ATSA can identify the sickle cell protein from normal protein, while the traditional TSA method cannot."
Another advantage of the ATSA is cost reduction in terms of human labor and equipment.
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email





