Hindering the production of Interleukin-1, could alleviate the symptoms of asthma such as mucus, swelling and constriction.
TOP INSIGHT
Interleukin-1 is involved in regulating the balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory T cells type 2 which triggers asthma.
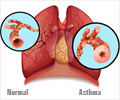
The allergic immune response, which triggers the symptoms of asthma, is a complex process, which starts with the over-activation of a certain white blood cell, the allergen-specific helper T cells type 2.
"We found that by adding a signaling molecule, Interleukin 1 (IL-1) using an experimental model of allergic asthma, the symptoms would worsen dramatically," explained Dr Caucheteux.
"Therefore by blocking production of IL-1, we could alleviate the symptoms, such as mucus, swelling and constriction."
Dr Jeff Zhu, Chief of the Molecular and Cellular Immunoregulation Unit at the Laboratory of Immunology at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said: "The finding that IL-1 is involved in regulating the balance between inflammatory and anti-inflammatory Th2 cells has not only significantly enhanced our basic knowledge on T cell biology, but also provided a potentially effective and novel strategy to treat asthma."
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email