A Brazilian specialist has warned that developing vaccines against the Zika virus would take at least three years.
Zika was previously only known to cause moderate cold and flu-like symptoms. But, increasing evidence indicates the virus may be connected to multiple neurological disorders, as well as microcephaly, a severe birth defect in which babies are born with smaller heads and brains. Global health experts agreed to prioritize developing vaccines against the Zika virus, but a Brazilian specialist warned that doing so would take at least three years.
"Perhaps in three years we will have a vaccine," Jorge Kalil, head of the Butantan Institute in Sao Paulo, told reporters in Geneva, acknowledging that even that estimate was 'optimistic'. He was among global health experts meeting in Geneva to determine what research and development should be prioritized in the fight against Zika, which has been spreading most rapidly in the Americas.
TOP INSIGHT
While global health experts agreed that efforts should focus on developing Zika vaccines, a Brazilian expert warned that doing so would take at least three years.
Experts have agreed that efforts should focus on developing vaccines particularly for women of child-bearing age, as well as on creating accurate diagnostic tests and innovative vector control tools to reduce mosquito populations, the World Health Organization said.
WHO's deputy director for health systems and innovation Marie-Paule Kieny told reporters work was under way to develop an emergency vaccine 'product profile' to help stake out regulatory requirements and help guide developers.
Kieny said, "The final profile should be ready in May 2016, but developing a usable vaccine would take much longer. Vaccine development is still at an early stage and the most advanced candidates are still months away from entering early human clinical trials."
"It is therefore possible that vaccines may come (too) late for the current Latin American outbreak," she said, stressing though that the development of a vaccine remains an imperative."
WHO said that 18 companies and research institutes were currently working on Zika vaccines. None have been tested on humans.
Another 31 labs are working on developing diagnostic tests, the global health body said, with a profile on the needed diagnostic tools expected to be ready by mid-April 2016.
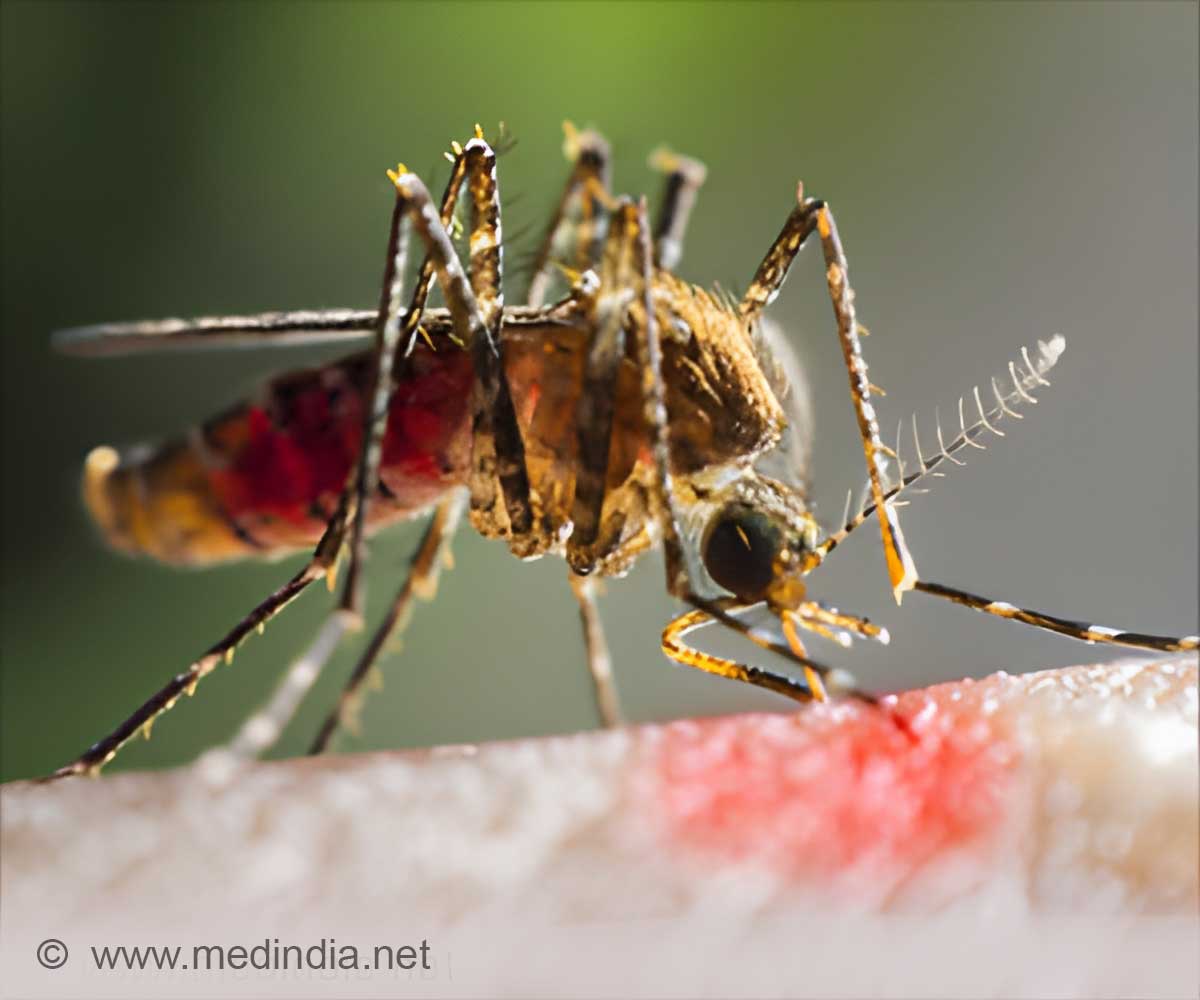
Next week, the WHO is set to convene a meeting of the world's top experts on vector control to determine if a range of radical new methods could also be safely and efficiently used against the Aedes aegypti mosquitos carrying Zika.
Such methods could, according to experts, include releasing genetically modified mosquitos, releasing large numbers of sterilized male mosquitoes to halt reproduction, or infecting mosquitoes with a bacteria that prevents their eggs from hatching and reduces their ability to transmit the virus.
WHO advised pregnant women not to travel to areas affected by the Zika outbreak, amid mounting evidence the virus causes birth defects.
Source-AFP
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email