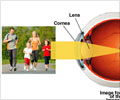
Attaining a higher level of education and spending more years in school are two factors associated with a greater prevalence and severity of nearsightedness or myopia, reveals a new study.

Researchers at the University Medical Center in Mainz, Germany examined nearsightedness in 4,658 Germans ages 35 to 74, excluding anyone with cataracts or who had undergone refractive surgery and found that myopia appeared to become more prevalent as education level increased.
The study found that 24 percent with no high school education or other training were nearsighted, 35 percent of high school graduates and vocational school graduates were nearsighted, while 53 percent of university graduates were nearsighted.
The researchers also found that people who spent more years in school proved to be more myopic, with nearsightedness worsening for each year of school. Furthermore, the researchers looked at the effect of 45 genetic markers, but found it a much weaker factor in the degree of nearsightedness compared to education level.
The study was published in the journal of the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Source-ANI
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email