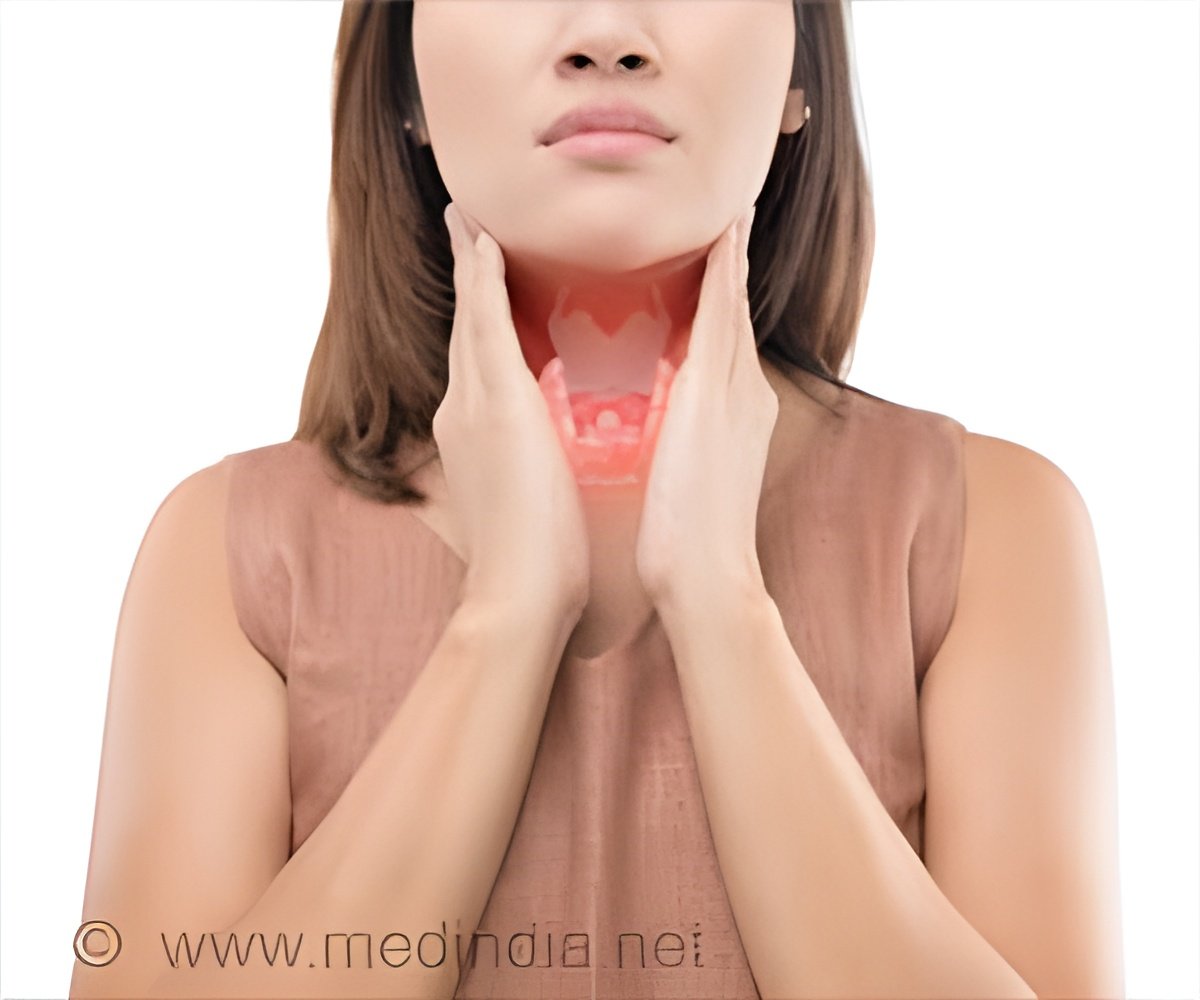
AI-driven new scoring system in thyroid cancer progression outperforms 'one-size-fits-to-all' tradition.
Optimized Dynamic Network Biomarker Deciphers a High-Resolution Heterogeneity Within Thyroid Cancer Molecular Subtypes
Go to source). New research from The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University tackles thyroid cancer by developing a groundbreaking AI biomarker system. This model uses an enhanced dynamic network biomarker (DNB) algorithm and identified a 'tipping point' in Stage II of DTC that shows a shift from an unchanging state to rapid progression.
TOP INSIGHT
Did You Know?
Just with 12 genes! How “miniPC” (a #simplifiedaibiomarker) offers a #personalizedapproach to #thyroidcancertreatment. #aipoweredbiomarkers #thyroidcancerprogression #medindia
TCPS Level: Discovering Individual Patient Risk
The team developed an automated scoring system called 'TCPS level' to estimate an individual patient risk that features early-warning molecular signals. “This score outperforms traditional staging in identifying high-risk individuals,” notes co-author Dr. Ge Zhang.The researchers applied AI-based consensus clustering to over 1,100 thyroid cancer samples and identified three reproducible molecular subtypes, each with distinct immune profiles and progression risks. The most aggressive subtype was associated with the gene ASPH, which was experimentally validated.
To support clinical use, they developed a simplified classifier (miniPC) based on just 12 genes, enabling accurate subtype prediction across multiple datasets. “This tool offers a practical approach to personalized treatment planning,” says Dr. Haonan Zhang.
By integrating multi-omics data, machine learning, and single-cell analysis, the study provides new insights and tools for early risk stratification and targeted management of thyroid cancer.
- Optimized Dynamic Network Biomarker Deciphers a High-Resolution Heterogeneity Within Thyroid Cancer Molecular Subtypes - (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mdr2.70004)
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email