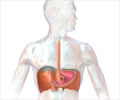
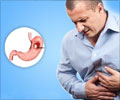
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Awareness Week observed from 20th - 26th November helps prevent complications by creating awareness among the public.
- November 19 - 25th is celebrated as GERD Awareness Week every year
- Nearly, seven million people have symptoms of GERD
- Heartburn can be prevented, and effective treatments are available for controlling GERD symptoms
GERD Awareness Week also coincides with Thanksgiving week. During this time, indulging in heavy meals, alcoholic beverages, and unhealthy food items can lead to heartburn and other GERD symptoms. Heartburn can be prevented, and effective treatments are available for controlling GERD symptoms.
TOP INSIGHT
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Awareness Week is observed from 20th - 26th November and is essential to help prevent complications of the disease.
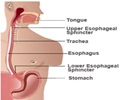
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic disease that can occur when the contents of the stomach contents repeatedly flow backward into the esophagus (food pipe).The population of U.S. is affected mainly by GERD, and about seven million people have symptoms of GERD. GERD can affect anyone, even infants and children. When left untreated can lead to severe health problems.
“Heartburn that happens more than once a week, worsens, or continues over time may signal a more serious condition like GERD,” said J. Patrick Waring, M.D., a gastroenterologist at Digestive Healthcare of Georgia in Atlanta.
Symptoms of GERD
The most common symptom is heartburn, and not all adults with GERD have heartburn. Other symptoms include:- Bad breath
- Nausea
- Pain in the chest or the upper part of the abdomen
- Difficulty in swallowing and
- Respiratory problems
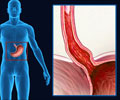
Complications of GERD
In severe GERD cases, the complications include:- Barrett’s esophagus
- Esophagal cancer - Presence of tumor cells in the tissues of esophagus
- Erosive Esophagitis - Inflammation and swelling of esophagus
- Esophageal Strictures - Gradual narrowing of esophagus resulting in swallowing difficulties
Treatment for GERD
GERD can be treated, but if not treated correctly, serious complications can occur. If there are symptoms of GERD patients need to consult a physician immediately. Sometimes, GERD can be treated with medication or surgery.The following are the tests that help in diagnosing GERD:
- Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy and biopsy
- Upper GI series
- Esophageal pH-impedance monitoring
- Esophageal manometry
Prevention of GERD symptoms
GERD can be prevented by changing your diet. As GERD Awareness Week coincides with Thanksgiving week, indulging in heavy meals, alcoholic beverages, and unhealthy food items can be avoided to prevent heartburn and other GERD symptoms.Tips to prevent the occurrence of GERD symptoms
- Consume smaller meals and have an early dinner
- Be physically active, as weight loss can help alleviate GERD symptoms
- Food should be seasoned lightly, as spicy foods can make the heartburn worse
- Avoid junk and fried foods, as they are more likely to aggravate symptoms
- Avoid citrus fruits and juices, as they are acidic and can worsen the symptoms
- Avoid chocolates, peppermint, caffeinated and carbonated beverages to avoid heartburn
- Quit smoking and reduce alcohol intake, as it can worsen the reflux
- Do not sleep within 3 hours after eating, as it can flare up the GERD symptoms
- Visit the doctor, for an accurate diagnosis to receive effective treatment
Myths and Facts About GERD
One out of every two adults would have had heartburn at some point in their life. There is a lot of misinformation about GERD. Here are some myths and facts about GERD.Myth 1: GERD is harmless.
Fact: Occasional heartburn is not severe, but chronic GERD can lead to various health problems. If left untreated, can cause asthma. The esophagus can be inflammated, due to the stomach acid leading to bleeding and ulcers in the throat. Some people might even develop Barrett's esophagus, which can lead to cancer later.
Myth 2: If there is no heartburn, then there is no GERD.
Fact: Heartburn is the most common symptom of GERD. However, people GERD can occur even without heartburn. Other symptoms are hoarseness, coughing, nausea and chest pain.
GERD awareness is essential to help prevent complications of GERD such as ulcers, throat and laryngeal inflammation, lung inflammation, strictures of the esophagus, and Barrett's esophagus.
Myth 3: Eating habits and lifestyle do not affect people with GERD.
Fact: Scientists are not sure as to what causes GERD. However, being overweight or pregnant, drinking alcohol or smoking have been linked to GERD. To reduce the symptoms of GERD, individuals need to lose weight, avoid alcohol, quit smoking, eat smaller meals, to stay awake for three hours after dinner, and avoid wearing tight clothes. Avoid consuming citrus fruits, tomatoes or tomato products, caffeine, spicy foods, garlic, onions, and mint.
Myth 4: Taking more antacids can relieve GERD symptoms.
Fact: Over-the-counter (OTC) antacids can be taken occasionally. However, side effects like diarrhea or constipation may be caused. Taking OTC remedies for more than twice a week or for longer can lead to various health problems. Therefore, consulting a doctor is essential.
References:
- The ABCs of GERD - (https://medlineplus.gov/magazine/issues/fall17/articles/fall17pg4-5.html)
- Acid Reflux (GER & GERD) in Adults - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/acid-reflux-ger-gerd-adults)
- Have You Heard? It’s GERD Awareness Week! - (https://www.sgna.org/Learn/The-Bottom-Line/have-you-heard-its-gerd-awareness-week)
- 15 Tips for GERD Awareness Week - (https://www.iffgd.org/press-releases/2013-1106-15-tips-for-gerd-awareness-week.html)
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email