Researchers have identified a genetic variant that can been linked with an increased risk of fatty liver disease in obese youth.
TOP INSIGHT
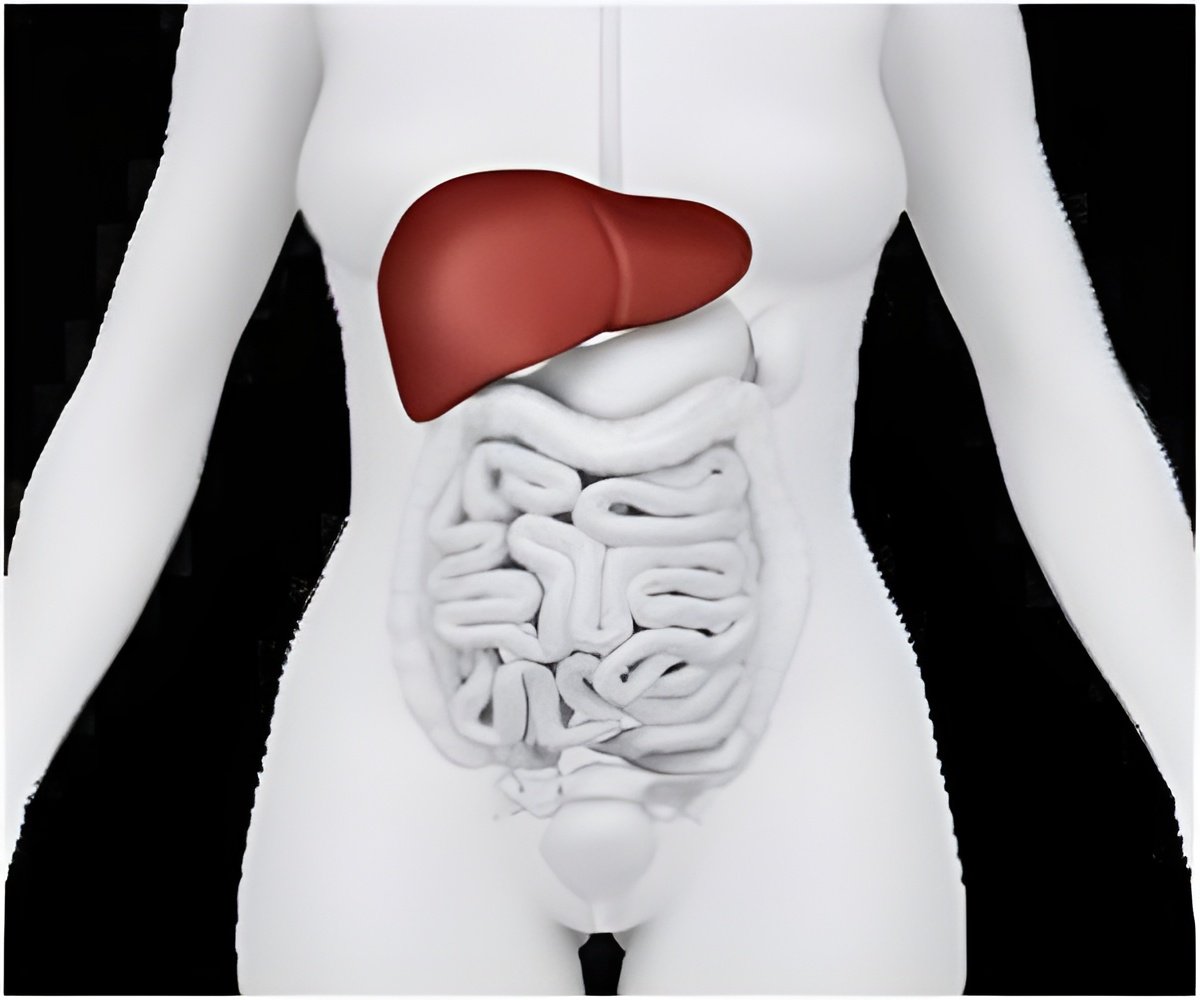
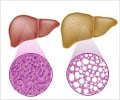
A genetic variant that codes for the transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2) protein has been linked with an increased risk of fatty liver disease in obese youth. The TM6SF2 protein helps regulate the liver's metabolism of fat, and predisposes obese kids to accumulate hepatic fat.
Dr. Nicola Santoro, senior author of the study, said, "The effect of the studied TM6SF2 gene variant on human metabolism is quite fascinating as it predisposes obese kids to accumulate hepatic fat, but at the same time it seems to protect them from cardiovascular complications. I think the future of this protein might be in the prevention and therapy of cardiovascular diseases."
The study is published in Hepatology.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email