With FDA's approval of BioThrax, we now have a vaccine that can be used together with antibiotic treatment, to prevent disease after exposure to anthrax spores.
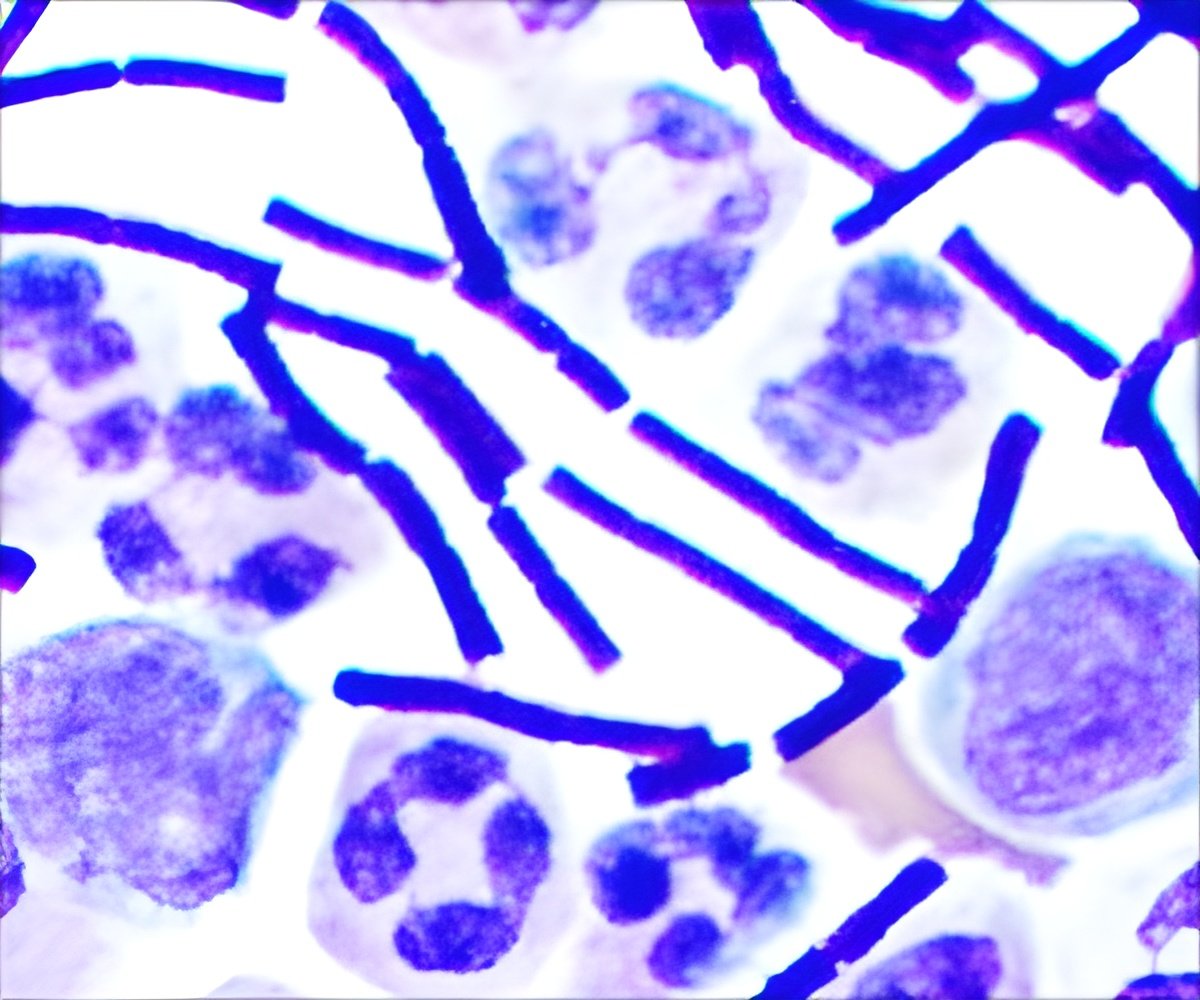
‘BioThrax is the first vaccine to be approved based on the USFDA’s “Animal Rule,” which allows animal efficacy data to be used as a basis for approval when human efficacy studies are not ethical or feasible.’





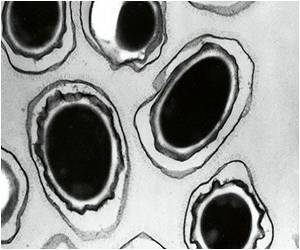
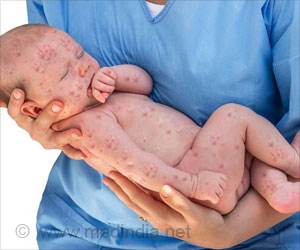
Researchers assessed levels of protective antibodies in the blood of rabbits and monkeys to predict efficacy to "predict efficacy in humans based on an assessment of the extent of antibody response achieved in human study participants.” Anthrax disease, especially the inhalation form, is often fatal if not promptly treated. Anthrax is considered one of the more likely agents to be used in a biological attack, primarily because its spores are very stable and easy to disperse.
Although it is rare, people may contract anthrax disease through natural exposures, such as contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
Infected rabbits treated with post-exposure antibiotic and BioThrax had a survival rate of 70 to 100 percent, depending on the vaccine dose administered.
The safety and antibody responses to BioThrax in humans were evaluated in a multi-center study conducted in the United States. The majority of study participants generated antibody responses that correlated to a 70 percent probability of survival that was observed in animal models.
Advertisement
Source-Medindia