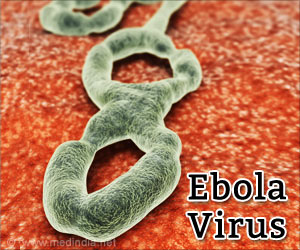
A Liberian woman was likely to be infected after she had sex with a man in March 2015. The man had Ebola symptoms in September 2014.
It was recently reported that a 44-year-old Liberian woman, who was likely to be infected from a 46-year-old man who had Ebola symptoms in September 2014, fell ill in March, a week after sex with him, and died, but another woman he had sex with around the same time tested negative. Kristen Nordlund, Center for Disease Control spokeswoman, said, "There have been fewer than 10 such cases and it’s been difficult to pinpoint that sex was the only way they may have been infected."
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA

 Email
Email