New treatment developed can completely kill a bacterial infection that can be deadly to cystic fibrosis patients, reports a new study.
TOP INSIGHT
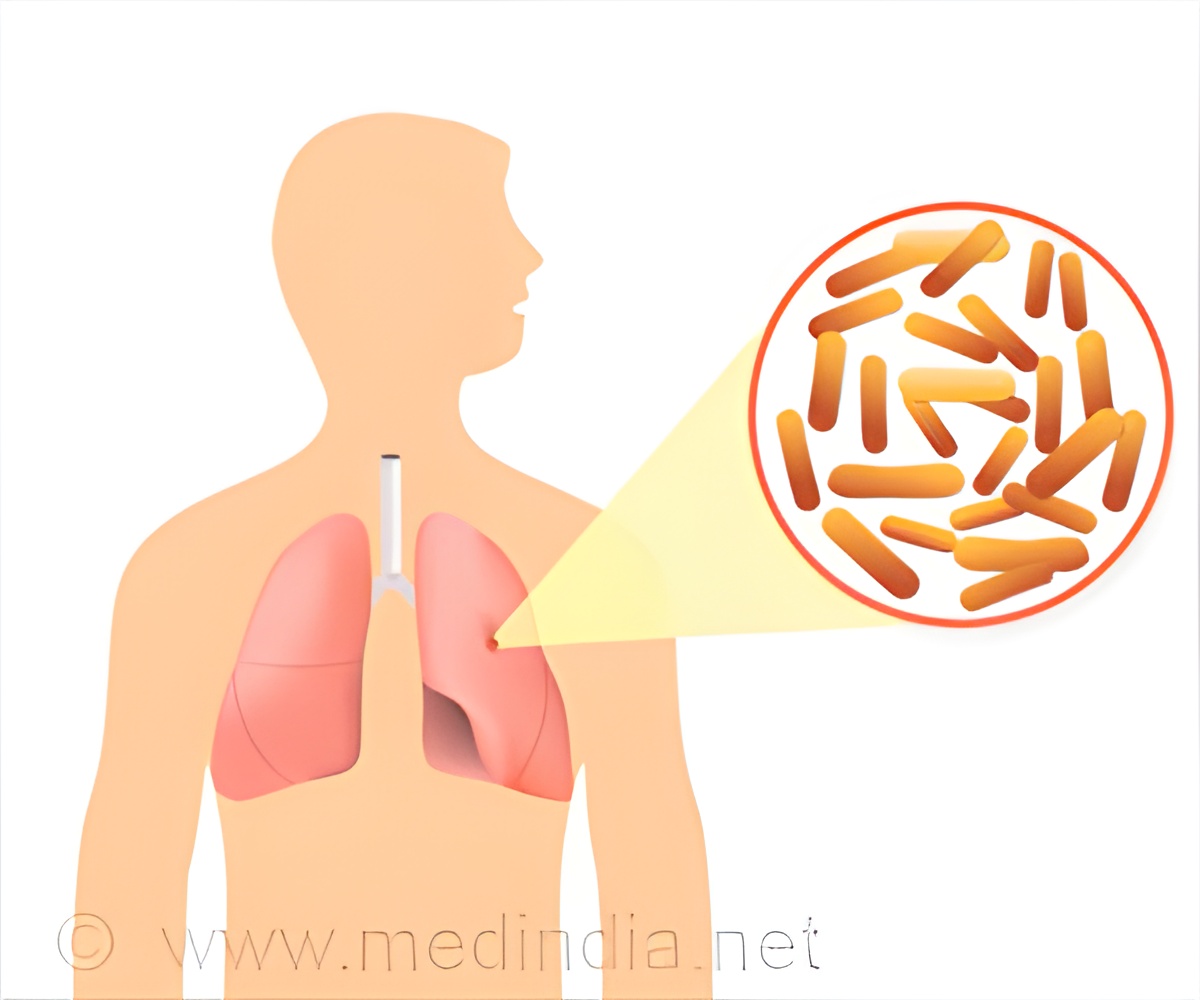
Mycobacterium abscessus is a bacterial pathogen from the same family that causes tuberculosis, which causes serious lung infections in people with lung disorders, most notably cystic fibrosis.
Read More..
Mycobacterium abscessus is highly drug-resistant. Currently, patients are given a cocktail of antibiotics that cause serious side effects including severe hearing loss and often doesn’t result in cure.
The researchers used samples of the pathogen taken from 16 infected cystic fibrosis patients and tested the new drug combination to discover how much was required to kill the bacteria. They found the amounts of amoxicillin-imipenem-relebactam required were low enough to be given safely to patients.
Until now, Mycobacterium abscessus has been virtually impossible to eradicate in people with cystic fibrosis. It can also be deadly if the patient requires a lung transplant because they are not eligible for surgery if the infection is present.
In the UK, of the 10,000 people living with cystic fibrosis, Mycobacterium abscessus infects 13% of all patients with the condition. This new treatment is advantageous not only because it kills off the infection, but it does not have any side-effects on patients, thus ensuring their quality of life and greatly improving survival chances for infected CF patients.
"This shows our drugs when used in combination, are widely effective and could, therefore, make a huge difference to people whose treatment options are currently limited.
The findings of this research will impact children being treated for the infection at Birmingham Children’s Hospital - who part-funded the research - but it can also be used nationally and further afield.
With more funding, the next stage of the research will be to test the treatment on more people with CF infected by this bacterium, comparing it to the antibiotics that are currently used.
Dr. Maya Desai, Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics, Birmingham Children’s Hospital, added: "This exciting development will significantly impact on the care of CF patients globally. It has been possible only with close collaboration between Aston University and Birmingham Children’s Hospital both from clinical research and financial point of view."
Dr. Paula Sommer, Head of Research at the Cystic Fibrosis Trust said: "It’s exciting that these lab-based studies investigating new antibiotic treatments for M. abscessus infection are showing such promise and adding to our expanding knowledge of this devastating bug.
"Mycobacterium abscessus, also known as NTM, is the most feared infection a person with cystic fibrosis can develop. Taking drugs to treat NTM can add to an already significant regime of daily treatments and take up to a year to clear infections. We look forward to a time when effective, short courses of treatment are available to treat NTM."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA



 Email
Email