The next decade will see a significant increase in the number of people living with osteoporosis and experiencing the devastating outcome of fragility fractures.
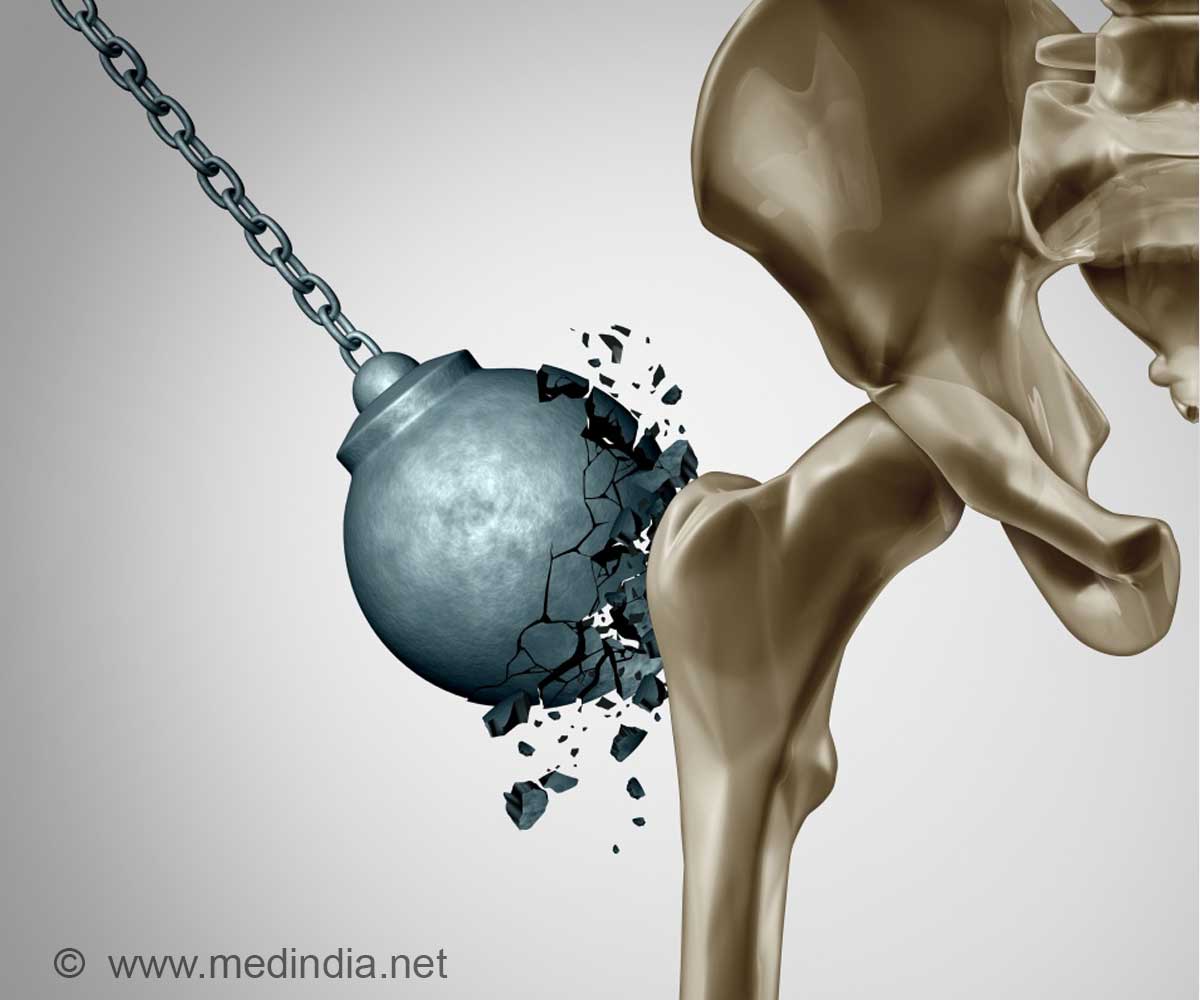
TOP INSIGHT
Key challenges which hinder efforts to improve bone health and provide optimal prevention of osteoporosis and fragility fractures, a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, have been reviewed by a new study.
The authors identify four distinct themes which encompass challenges related to: (1) case finding and management of individuals at high risk of fracture; (2) public awareness of osteoporosis and fragility fractures; (3) reimbursement and health system policy; and (4) epidemiology of fracture in the developing world.
Co-author Professor Eugene McCloskey, Director of the MRC ARUK Center for Integrated Research in Musculoskeletal Ageing, Metabolic Bone Center, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, UK., stated, "This review identifies, among other challenges, the current gaps in delivery of best clinical practice, low levels of public awareness, and insufficient access and funding for diagnosis and treatment. Sadly, these gaps are a clear reflection of the low priority currently given to bone health and fracture prevention in healthcare policy."
Several of the main challenges and solutions identified are:
- An urgent need for increased implementation of systematic approaches to prevent secondary fractures. Strategies and models of care such as Fracture Liaison Services, which improve the identification and treatment of individuals who have already sustained a first fragility fracture, are shown to be highly effective;
- In terms of public awareness, there is a need for greater awareness of the life-changing and life-threatening impact of fractures due to osteoporosis. Given the extremely high rates of non-adherence to medication, it is essential that more support be given to patients and their doctors to have meaningful discussions concerning the risk-benefit ratio of osteoporosis treatment;
- In many parts of the developing world, robust epidemiological data to quantify fracture incidence is still needed. This will be a critical step towards developing fracture prevention policies for regions such as Asia and Latin America, which have rapidly ageing populations.
Professor Cyrus Cooper, Chair of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) Committee of Scientific Advisors, stated: "We cannot afford to ignore the current and growing burden that osteoporosis and fragility fractures impose upon societies around the world. As we now have the knowledge and tools needed to manage bone health optimally, I urge healthcare professionals, stakeholder organizations, and healthcare authorities to make a concerted effort to implement these tools. Prioritization of fragility fracture prevention must become a reality worldwide."
The review "Mind the (treatment) gap: a global perspective on current and future strategies for prevention of fragility fractures" is an updated, referenced synopsis of the IOF illustrated report "Gaps and Solutions in Bone Health - A Global Framework for Improvement" which was published in nine languages on the occasion of World Osteoporosis Day.
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email