Researchers led by UCLA have found that changes in the treatment for the most common form of heart attack have led to higher survival rates among men and women.

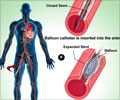
Heart attacks are broadly classified into two types. The more severe form, ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), involves complete blockage of an artery supplying blood to the heart muscle. The less severe type, NSTEMI, involves partial or temporary blockage of the artery. Studies in the U.S. and Europe have found that although the incidence of STEMI heart attacks is declining, the number of NSTEMI heart attacks increased in the past decade. Guidelines issued in 2012 by the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association recommended initiating cardiac catheterization in high-risk NSTEMI patients within 12 to 24 hours after the patient arrives at the hospital.
This strategy had been evolving since 2009 following publication of the Timing of Intervention in Acute Coronary Syndromes trial. Previously, the recommendation was to begin catheterization in high-risk NSTEMI patients within 48 hours. Fonarow and his colleagues examined trends in the use of cardiac catheterization for people who had been hospitalized after suffering an NSTEMI, within 24 hours and within 48 hours of presentation, seeking to determine whether changes in their care may have resulted in better outcomes. The researchers analyzed publicly available records from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, the largest U.S. database of hospitalized individuals. Of the 6.5 million patients whose records they examined, 3.98 million were admitted to hospitals with NSTEMI diagnoses. The study tracked the proportion of those patients who underwent cardiac catheterization each year, and their outcomes — how many died in the hospital, the average length of their hospital stays, and the cost of hospitalization. They found that as the trend toward earlier intervention in NSTEMI patients took hold — with doctors beginning treatment within 24 hours after patients arrived at the hospital, rather than within 48 hours — the rate of in-hospital death declined from 5.5 percent in 2002 to 3.9 percent in 2011. Improvements were found for men and women, older and younger patients, and across all races and ethnic groups. In addition, the average length of patients' hospital stays decreased during the decade-long study, from 5.7 days to 4.8 days. NSTEMI patients who underwent cardiac catheterization within the first 24 hours had the shortest average stays. Although more NSTEMI patients in all demographic groups received early cardiac catheterization as the study progressed, there were still significant differences across age, gender, and racial and ethnic groups in how frequently early intervention was used. Men, for example, were more likely to receive earlier catheterization than women. "Despite the improvement, there are significant differences in the age-, gender-, and ethnicity-specific trends in the use of invasive management of NSTEMI, and these findings may help guide further improvements in care and outcomes for male and female patients of all ages, races and ethnicities," said New York Medical College's Dr. Sahil Khera, the study's first author. "Further efforts are needed to enhance the quality of care for patients with NSTEMI and to develop strategies to ensure more equitable care for patients with this type of heart attack."
Source-Eurekalert
 MEDINDIA
MEDINDIA


 Email
Email